concept
Habitat
- A place where living organism lives is called habitat
Types of habitat:
- Terrestrial Habitat : ones that are found on land, like forests, grasslands, deserts, shorelines, and wetlands.
- Aquatic Habitat : All water bodies such as reservoirs, lakes, water streams, rivers, ponds, estuaries, wetlands, and sloughs.
- Arboreal habitat : organisms that use trees for their living.
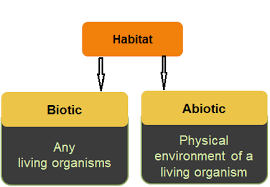
COMPONENTS OF HABITAT
- Habitat provides food, water, air, shelter, and the other requirements needed for the organism. Various types of plants and animals share the same habitat. Habitat has two components - biotic and abiotic components.
There are two major types of habitats which are:
- Terrestrial habitat
- Aquatic habitat
The terrestrial habitat includes the desert habitat, the forest or the grassland habitat, and the mountain habitat.
The aquatic habitat can be fresh water or marine habitat. Fresh water habitat includes ponds, lakes, and rivers, while the marine habitat includes seas and ocean.
Adaptation
- Tendency of an organism to develop certain specific features which improve the chances of its survival in the environment in which it lives is known as adaptation.
- Two Types:
- Permanent Adaptation: genetic basis , causes permanent changes in the individuals.
- Temporary adaptation: A short term , not inherited
Adaptation to desert Habitat:
- Desert is dry and hot.
- Animals which survive in deserts are insects, birds, reptiles , small mammals like Camels.
- Nocturnal :Animals that show the tendency of inactive during the day and become active during the night. This is just to prevent loss of water from their body.
- Hibernation: Animals that show the tendency of hide themselves in burrows with gelatinous secretions and sleep for eight to nine months in a year.
- Camel:
- ship of the desert
- hump of the camel is a reservoir of food.
- can drink 40 liters water in 10 minutes and store it in water-cells, muscles and connective tissues.
- It can live without drinking water for about 2 weeks.
- Desert plants: grow under very poor water conditions known as xerophytes.
- cacti and opuntia
- Cacti plants can store water in their spongy stems. These are known as succulent plants.
Adaptation to Mountainous Habitat:
- very cold and windy climate. snowfall is common in winters.
- Trees are cone shaped and have sloping branches and have needle like leaves that help the rainwater and snow to slide off easily.
- Pine and Deodar trees are example
- Mountain Animals:
- usually white or light coloured.
- thik skin or fur to protect them from cold.
- Long hairs to keep them warm.
- Yaks, snow leopard , mountain goats are example
- strong hooves
Adaptation to Greenland Habitat:
- One fourth of the earth's land.
- Tropical grasslands are hot throughout the year.
- Temperate grasslands are hot in summer and very cold in winters.
- Animals are mostly Herbivorous. Cow , Deer, Goat etc.
- Carnivores like Lion, Tiger , Hyena also found in grasslands.
Adaptation to Aquatic Habitat:
- Animals live in water
- Frogs and duck have webbed feed for swimming.
- Dolphin and Whales do not have gills. They breath through nostrils or blowholes.
- Usually sea animals stay near seabed.
- Aquatic plants of fresh water are called hydrophytes.
- stems of these plants are long , hollow and light.
Organism
Any living entity, from tiny bacteria to enormous elephants and everything in between, is simply referred to as an organism. There are various kinds of flora and animals in various places. For instance,
- Deserts include cacti and camels as vegetation.
- Crabs and palm trees can be seen on beaches.
- The sea is home to fish and other aquatic creatures.
Characteristics of Living Organisms
- Nutrition: It is the process through which animals receive food and use it for all of their activities. Each organism needs nutrition to gain energy. Plants/tress who make their food themselves are called producers or autotrophs.
- Growth: Every living being grows and shows growth in diverse ways. Its body cells divide and grow to facilitate growth in an organism. Property of plant to move towards light is called phototropism. Property of plant to grow roots vertically downwards due to gravity on plants is called geotropism.
- Respiration: It is the process of inhaling and exhaling in a living organism. All living things require breathing to survive. The body finally gets energy from the food it consumes through breathing. Different methods for the exchange of gases, a step in the respiration process, may exist in some animals.
- Excretion: Every living creature needs nourishment. Not all of the food consumed is really utilised. It is only partially used by the body. Food that is leftover or unfinished becomes waste and must be eliminated. In other bodily functions, our bodies also create wastes like urea. All of this waste material is eliminated by living things through a process called excretion. The process of removal of wastes in plants is called secretion. Rubber plant, calotropis , excrete Latex ( a white sticky thick liquid ), Latex is the source of natural rubber.
- Reproduction: It is the process by which all living things create new members of their own species. Distinct plants and animals may have distinct reproductive methods. Some creatures lay eggs to hatch their young. Young are born to some animals. The seeds that are produced by plants grow into new plants. Other than seeds, certain plants can also reproduce by other organs. Producing young ones of its own kind is called reproduction.
- Response to Stimuli: Stimuli are changes in our environment that cause us to react to them. Every living thing responds to changes in its environment. All living organisms respond to stimuli such as temperature, touch, light , sound , smell etc. for example : high temperature of the object is stimulus and quick withdrawn of hand on feeling high temperature is response.
- Movement: Animals move around and display a variety of different body movements. In order to prevent movement from one location to another, plants are typically anchored in the soil. However, different elements like water, minerals, and the food that plants synthesize migrate from one area to another. Other types of movement are also displayed by plants, such as the opening and shutting of flower buds.
- The movement of an organism, bodily from one place to another is called locomotion.
- The movement of plant in the direction of stimulus is called tropism.
- Bending of stem towards sunlight is called phototropism.
- Movement of roots vertically downwards towards the earth, geotropism.
- Opening and closing of guard cells of stomata to control water level in leaves , hydrotropism.
- Movement of plant neither in the direction nor away from the stimulus is called nasticism.
- Lotus -> Hydrophytes
- Dry Habitat -> Camel
- Gum -> Acacia
- Cold region -> Polar Bear

