Concepts
The French Revolution
- 14 July 1789:- A time of social and political upheaval in France ( फ्रांस में सामाजिक और राजनीतिक उथल-पुथल का समय )
- Inspired by liberal and radical ideas, Its overthrow of the Monarchy influenced the decline of absolute Monarchies in other parts of Europe. ( उदारवादी और कट्टरपंथी विचारों से प्रेरित होकर, राजशाही को उखाड़ फेंकने , यूरोप के अन्य हिस्सों में पूर्ण राजशाही के पतन को प्रभावित किया।)
French Society During the Late 18th Centaury
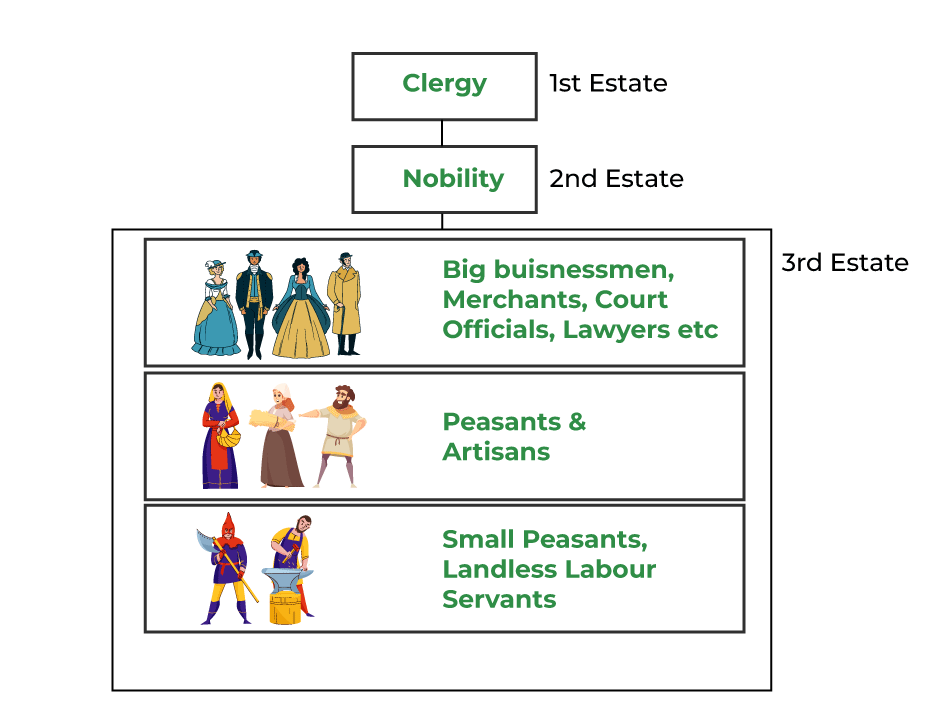
- Divided into three classes, which were known as Estates.
- Subsistence crisis in France during the old regime
- The three causes which led to the subsistence crisis in France are as follows
1) The population of France rose from about 23 million in 1715 to 28 million in 1789. This led to a rapid increase in the demand for food grains. Production of grains could not keep pace with the demand. So the price of bread which was the staple diet of the majority rose rapidly.
2) Most workers were employed as labourers in workshops whose owner fixed their wages. But wages did not keep pace with the rise in prices. So the gap between the poor and the rich widened.
3) Things became worse whenever drought or hail reduced the harvest. This led to a subsistence crisis, something that occurred frequently in France during the Old Regime.
- The three causes which led to the subsistence crisis in France are as follows
- The circumstances leading to the outbreak of revolutionary protest in France
-
Social Inequality: French society in the eighteenth century was divided into three estates namely The Clergy, The nobility and third estates which comprise peasants, officials and small business. It was only third estates that pay taxes. Clergy and nobility were exempt from taxes.
-
Subsistence Crisis: The population of France also increased from 23 million in 1715 to 28 million in 1789. Food grains were now in great demand. Price of bread shot up. Wages did not keep pace with rising prices. This led to subsistence crisis.
-
Economic Problems: Long years of war had drained the financial resources of France. France had a debt of more than 2 billion livres. To meet its regular expenses, such as the cost of maintaining an army, the court, running government offices or universities, the state was forced to increase taxes.
-
Strong Middle Class: The middle class emerged educated and wealthy during the eighteenth century. They believed that no group in society should be given privileges by birth. Ideas of equality and freedom were put forward by philosophers. The ideas of these philosophers were discussed intensively in salons and coffee houses and spread among people.
-
Immediate Causes: On 5 may, 1789, Louis XVI called together an assembly of Estates General to pass proposals for new taxes. Third estates protested against this proposal but as each estate have one vote, the king rejected this appeal. They walked out of the assembly.
-
- The social contract theory was proposed by Rousseau. Jean-Jacques Rousseau was a Genevan rationalist, author, and arranger.
- Jacobin Club, a revolutionary political movement that was the most famous political club during the French Revolution (1789–1799). The club got its name from meeting at the Dominican rue Saint-Honoré Monastery of the Jacobins.
- Tithe was a tax levied by the church comprising one-tenth ( 1/10th ) of the agricultural produce.
- Taille was a direct land tax.
- Chateau was a state/residence belong to a king or a nobleman.
- Manor is an estate consisting of the lord's lands and his mansions.
- French Revolution introduced the principles of "Liberty, Equality and Fraternity" to the world.
- In France, the red cap worn by the San Culottes symbolised Liberty and freedom. Sans Culottes wore a red cap as a symbol of Liberty in France. The "Cap of Liberty," as it is known, can be found on the flags of Paraguay, Santa Catarina, and several other countries.
- In 1689 , John Locke wrote the book ' Two Treaties of Government'.
- Political symbols of France:
- Symbol of Royal power - Scepter ( राज-दंड )
- Personification of the law - The wings of the woman ( Winged Woman)
- Rays of Knowledge - The eye within a triangle radiating light.
- The rays of hope - The broken chain ( symbol of freedom )
- Symbol of Unity - A bundle of rods or fasces
- Symbol of Eternity - A snake biting its tail to form a ring
- The National colours of France - Blue-white -red
- Women were disappointed by the French constitution 1791 because they were not granted Right to vote.
- Males who are above 25 are only considered active citizens. Passive citizens- Passive citizens consist of citizens who are illiterate and have no knowledge of the government and law. These citizens are below 25 years of age. They are under the protection of the government and don't pay taxes.
- The everyday life of the French people was affected strongly by the revolution. With the abolition of Censorship and the Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen, Freedom of Speech became a natural right of people.
- On 3 September 1791, the National Constituent Assembly forced King Louis XVI to accept the French Constitution of 1791, thus turning the absolute monarchy into a constitutional monarchy.
- The period of the French Revolution from 1792-1793 is called the Reign of Terror. Robespierre, the leader of the Jacobin club, used a revolutionary tribunal to arrest people who seemed to be against the republic nation. They were guillotined, when found guilty.
- Robespierre was the leader of jacobins club. he was born on 6 may 1758 and died on 28 July 1794. his reign is referred as the reign of terror because during that time guillotined system was used and 1400 people were died during this period. he followed a policy of severe control and punishment

