Concepts
- All living organisms need energy to perform various activities. They obtain this energy from the food they eat. Energy is stored in the food materials as chemical energy. Digestion process break downs the food into smaller soluble molecules inside the living organism body. These smaller molecules then react with oxygen inside the cell to release energy to perform several activities in their life and helps in the growth.
- Nutrients - The process of taking food and its utilization by the body is called nutrition. Certain substances are present in the foods that help in the survival of the organisms. These special substances are called nutrients for example, proteins, vitamins, carbohydrates, minerals and fats.

Figure 1: Different Nutrients
Mode of Nutrition in Plants:
- Autotrophic Nutrition: The mode of nutrition in which the organism makes its food itself from simple inorganic substances is called autotrophic nutrition.
- Autotrophic Organisms - They can prepare their food by themselves such as plants
- Organism who make their own food are known as Autotrophs. Autotrophs are producers of food so they are also called producers. The mode of nutrition in green plants is autotrophic.
- Heterotrophic Nutrition: The mode of nutrition in which the organism can not make their food and depend on others for their food is called heterotrophic nutrition.
- Heterotrophic Organisms - They depend upon other organisms for their food such as animals.
- All animals and humans are heterotrophs.
- Heterotrophs can be divided into three types:
- Herbivores ( Plant Eaters ) : The animals which eat only grass , plants or plant products. Ex.; Elephant , Camel, Cow , Deer , Goat , Grasshopper etc..
- Carnivores ( Meat Eaters ) : The animals which eat only meat or flesh of other animals Ex.: Lion, Tiger , Jackal , Hawk, Frog , Snake , Vulture , Lizard.
- Omnivores ( Plant & Meat Eaters ) :The animals which eat both plant & meat. Ex.: Humans , Crow , Dog , Ant , Sparrow , Mynah. Man is an omnivore.
How do plants prepare their food?
Plants prepare their food with the help of certain raw materials that they gather from their surroundings:
- water
- carbon dioxide
- sunlight
- minerals
- chlorophyll
The process by which plants prepare their food by using these raw materials is called Photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis is described by the following reaction:

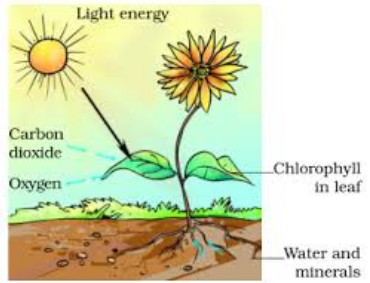
Figure 2: Photosynthesis
Where is the food made in plants?
- Leaves are also known as the Food Factories of the plants as they are the places where food is prepared.
- Different parts of the plants like roots gather the raw materials from the environment and then transfer them to the leaves where photosynthesis takes place.
- Transportation of water and Minerals in plants - The roots of the plants absorbs the water and minerals of the soil and then transports them to the leaves via stems and branches.

Figure 3: Transportation of water and Minerals in plants
-
Inhalation of Carbon Dioxide - There are tiny holes or pores present on the surface of the leaves called Stomata that take in the carbon dioxide present in the atmosphere.

Figure 4: Stomata on leaves and the Chlorophyll
-
Presences of Chlorophyll in the Leaves - A substance called Chlorophyll is present in the leaves of the plants. It is a green colour pigment. The chlorophyll not only provides green colour to the leaves but also helps in the process of photosynthesis. Chlorophyll captures the sunlight and along with other raw materials prepares the food in the leaves.
-
This process of photosynthesis only occurs in the daytime in the presence of Sunlight hence it is called Photosynthesis, photo means light.
Why sun is called the ultimate source of energy for all living organisms?
We know that the plants use solar energy to make their food. The herbivores animals depend upon the plants for their food. Animals (carnivores) that do not eat plants depend upon the herbivores animals. Therefore, all of the living organisms directly or indirectly receive their energy from the Sun.
Cells in Living Organisms
All living organisms are made up of tiny structures called cells. Some organisms (microscopic) contains only one cell while others plants and animals contain many cells of different kinds. Parts of a cell:
- The Nucleus - Every cell has a nucleus present in the centre that performs various functions of the cell.
- The Cell Membrane - Every cell has an outer boundary which protects the cell called the Cell Membrane.
- The cytoplasm - Every cell has a gel-like structure present in it called the Cytoplasm.
- Cell organelles: These are membrane bound structures found within a cell in the cytoplasm. The cell organelles have special function associated with them. Different cell organelles found in the cell are:
- Mitochondria – Produces energy for the cell
- Endoplasmic Reticulum – Produces lipids and proteins in cell
- Golgi apparatus – Helps in exporting materials out of cell
- Lysosomes – Help in digestion in the cell

Figure 5: Structure of Cell in Animals and Plants
Can photosynthesis take place in other parts of the plant?
Yes, green stems and branches of the plants can also undergo the process of photosynthesis. For example, plants in the desert area like cactus do not have leaves but they still exist there because their stem produces the food for the plant.
Why is the process of photosynthesis important?
- There will be no food if the plants would stop conducting the photosynthesis process.
- The plants take in carbon dioxide and produce oxygen during the process of photosynthesis. Hence, without this process, it would not be possible to survive on earth as they would be no oxygen.
Production of Oxygen and Carbohydrates by the Plants

Figure 6: Production of Oxygen and Carbohydrates
Plants use carbon dioxide and water in presence of the sunlight and chlorophyll to produce carbohydrates and oxygen. The carbohydrates thus produced by the plants are converted into starch.
Chloroplast and the Process of Photosynthesis

Figure 7: Structure of Chloroplast
- Chloroplasts are special cell organelles that are found only in plant cells. They are called the food producers of the plant cells.
- The chloroplasts are surrounded by two membranes called the Inner and Outer Membrane. The inner membrane surrounds stroma and thylakoid stacks.
- The chlorophyll molecules are present on each of the thylakoids. The chloroplasts convert the sunlight into sugars that are used by the plant cells.
- Hence, chloroplasts allow the conduction of the process of photosynthesis. The chlorophyll that can absorb the sunlight is present inside the chloroplasts.
- When the light of the sun hits the chloroplasts and the chlorophyll, the light energy is converted into chemical energy found in compounds such as ATP and NADPH.
- Then these energy molecules move into the stroma where carbon dioxide is attached to them. As a result of the molecular reactions, oxygen and glucose are created.
Can leaves which are red or Brown or violet in colour conduct photosynthesis?
Yes, the chlorophyll is also present in leaves that are not green in color. They are of different colours because the other colour pigments are more than the green colour pigments in such leaves.
Algae contain chlorophyll
Algae are green coloured organisms found in the stagnant water. They get their green color from chlorophyll. Since they have chlorophyll in them they are capable of conducting photosynthesis. (olympiads)

Figure 7: Algae in Water
How do plants generate proteins and fats?
- Along with carbohydrates, plants can also produce proteins and fats which are formed with the help of Nitrogen.
- Nitrogen is present in large amounts in the air but plants cannot consume the nitrogen directly from the atmosphere.
- The soil often contains some bacteria that are capable of converting the nitrogen into nitrates which can be the used by the plants.
- Also, fertilizers used by farmers and gardeners contain a high amount of Nitrogen which mixes into the soil and is used by the plants.
Nutrition in Plants that do not contain Chlorophyll
Many plants do not contain any chlorophyll. Hence they are unable to prepare their food by themselves. Therefore, they rely on other plants and animals for their food. Thus the plants which do not contain chlorophyll are heterotrophs and the mode of their nutrition is heterotrophic.
Types of heterotrophic nutrition :
- Saprophytic nutrition
- Parasitic nutrition
- Insectivorous nutrition
- Symbiotic nutrition
Saprophytic nutrition : The plants which derive their food from the dead or decaying organic matter are called Saprophytes.
- This mode of nutrition is called saprotrophic nutrition and the organisms that survive because of the saprotrophic nutrition are called Saprophytes. and these types of organisms are known as Saprotrophs.
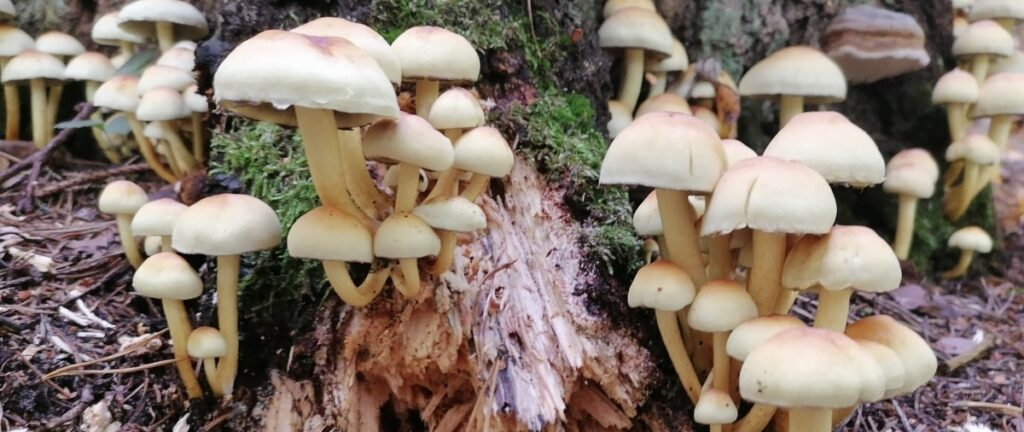

How do saprophytes obtain their nutrition?
- The saprophytes secrete digestive juices on the decaying and dead matter.
- These juices convert the matter into a solution.
- The saprophytes that absorb the nutrients from the solution.
- For Example, Fungi (yeast and mushrooms) are a saprophytes that can be found on stale food and pickles which are exposed to the hot and humid environment.
- fungi (ex. bread mould) is also example of this:

Parasitic nutrition : The mode of nutrition in which plants derive their food from the bodies of some other green plants and animals is called parasitic. The green plant or the animal which provides the food is called the host.
- Plants such are Cascuta ( Amarbel ) , Apodanthes , Certain bacteria and Fungi are totally parasitic.

Yellow color Cuscuta plant growing over green plants
- The plants which make a part of their food themselves by photosynthesis but derive other components such as water , minerals from other hot plants are called partial parasitic. Mistletoe plant is example of partial parasitic.
Insectivorous nutrition : The mode of nutrition in which green plants derive their own food but also depends on insects for nitrogenous food is called insectivorous nutrition.
Some plants such as pitcher plants depend upon insects for the food and thus are called Insectivorous. The leaves of these plants are modified into a pitcher like structure. The top part of the leaves acts as a lid which can open and close the pitcher. The pitcher contains hair in a downward direction which traps the insects. The pitcher on capturing the insect secretes some digestive juices which help in the digestion of the insect. For Example, Dischidia and Nepenthes

Insectivorous Plants
Symbiotic nutrition : The mode of nutrition in which two plants live together as a part of the same plant and mutually help each other are called symbionts. Such relationship is called symbiosis. and such mode of nutrition is called Symbiotic nutrition.
Examples of organisms living in a symbiotic relationship: fungus ( saprophyte ) + alga ( autotroph ) = Lichen ( symbiotic )
- Some fungi live in the roots of the trees. These fungi take food from the trees and in return help the trees in absorbing water and nutrients from the soil.
- Sometimes an organism that contains chlorophyll such as algae lives in association with a fungus (together called as Lichens). The algae provide food and nutrition to the fungus while the fungus provides water, minerals and shelter to the algae.

Lichens
Replenishing the Soil with Nutrients ( by using manure , by using fertilizers , by crop rotation method )
- Plants get their nutrients from the soil mainly hence there is a need to replenish the soil again with nutrients so that the plants can survive on it.
- Fertilizers and manure are often used to replenish the soil with the nutrients. They contain potassium, phosphorus and nitrogen all of which are important for the plants.
- A bacterium called Rhizobium is present in the soil which can convert nitrogen present in it in the form that can be consumed by the plants.
- The rhizobium generally lives in the roots of the plants such as peas, beans, grams and legumes and provides nitrogen to these plants. This again is an example of a symbiotic relationship. The farmers often do not need to use fertilizers while growing such crops. (Olympiads)

Rhizobium Bacteria in Soil
- Gram , Peas , Moong , Beans etc. are legumes. The roots of these crops have nodules on them. These nodules have symbiotic bacteria. These bacteria have a property to convert atmospheric nitrogen into nitrates. Nitrates are soluble in water and can provide nitrogen to plants. Thus Rhizobium can convert atmospheric nitrogen into soluble salts of nitrogen.

