Key Concepts
Understand Fundamentals
- The light coming from the sun gets reflected from the surface of the Earth is called Earth Light.
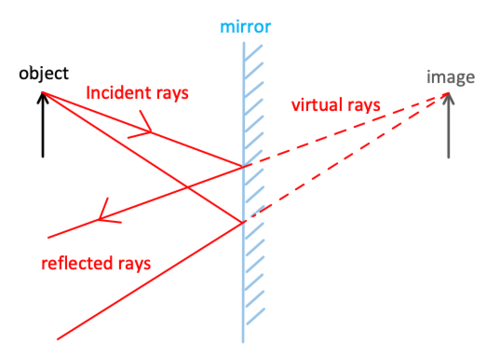
- When light falls on an object or any surface, it may pass through it , it may get absorbed by it or it may bounce back after striking the object. The bouncing back of the light rays from the surface of an object is called reflection.
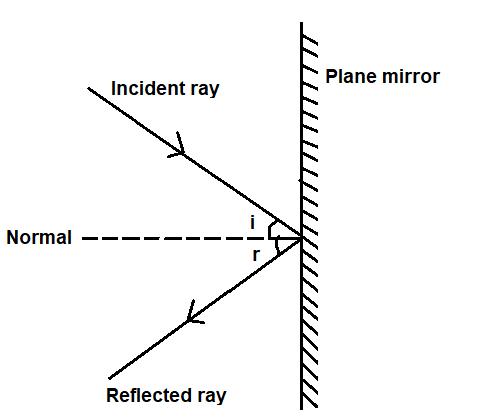
- The ray of light which falls on an object is called incident ray of light.
- The ray of light which gets bounced back is called reflected ray of light.
- The angle between the incident ray and the normal at the point of incidence is called angle of incidence (< i ).
- The angle between the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence is called angle of reflection (< r ).
- A smooth m highly polished reflecting surface is called a mirror.
- Laws of reflection:
- Law-1: angle of incidence (< i ) = angle of reflection (< r )
- Law-2: The incident ray , the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
- Reflection of light from a smooth mirror is called regular reflection.
- Reflection of light from a irregular or rough surface is reflected in different direction. This type of reflection is called irregular or diffused reflection.
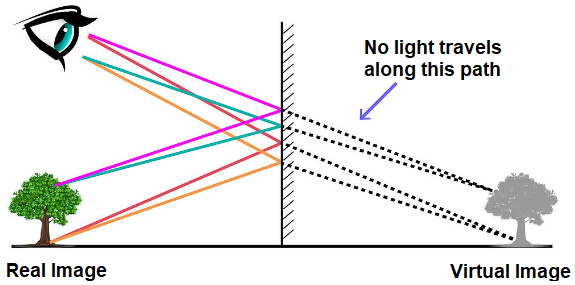
- When the rays of light after getting reflected from a mirror actually meets at a point, a real image is formed. A real image can be obtained on a screen. So, the image which can be obtained on a screen is called a real image.
- When the rays of light after getting reflected from a mirror appear to meet at a point, a virtual image is formed. Such image can not be obtained on a screen. So, the image which can not be obtained on a screen is called a virtual image.
- The images formed by a plane mirror are virtual images.
- A concave mirror gives a real image when object is placed at it focal point or beyond.

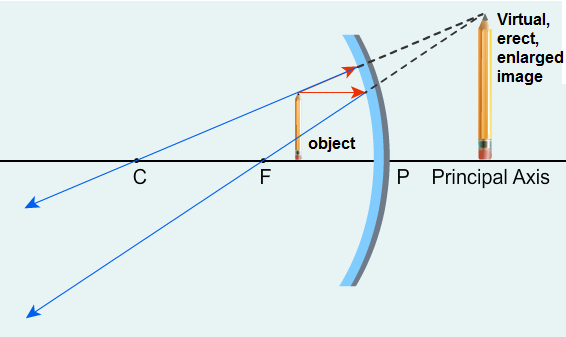
- A concave mirror gives a virtual image when object is placed at distances less than its focal length.
- A convex mirror always forms a virtual image of the object placed before it.
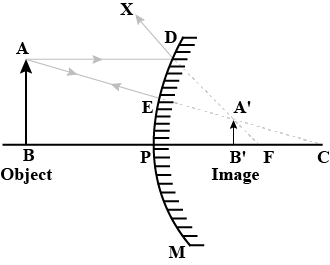
- Formation of image in a plane mirror is virtual , of the same size of the object , laterally inverted , as far behind the mirror as the object is in front.
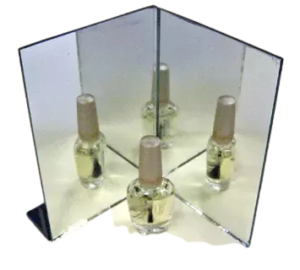
- When the two mirrors are places at right angle to each other , three images are formed.
- When the two mirrors are placed Parallel to each other , infinite number of images are formed.

- Plane mirrors are commonly used
- as a dressing mirror
- for making kaleidoscope and periscope
- as a reflector in solar cooker
- Kaleidoscope is based on the principle of multiple reflection from a set of three mirrors inclined at each other at 60 degree.
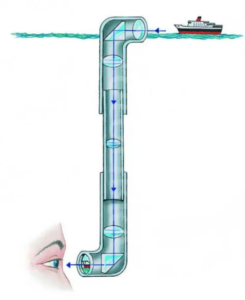
- Periscope is a device which is used for seeing objects which are not in direct line of sight, such as to see ships on the surface of water from a submarine.
- When white light passes through a glass prism, it separates into its spectrum of seven colors (in order violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange, and red), a process known as Dispersion of Light.
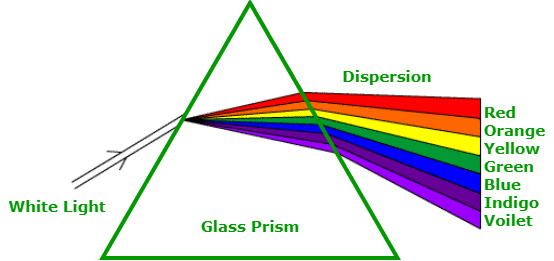
- Red light travels the fastest , and the violet light the slowest of all seven colors.
- The Human eye resembles a camera in many ways.The main parts of the eye are shown below:
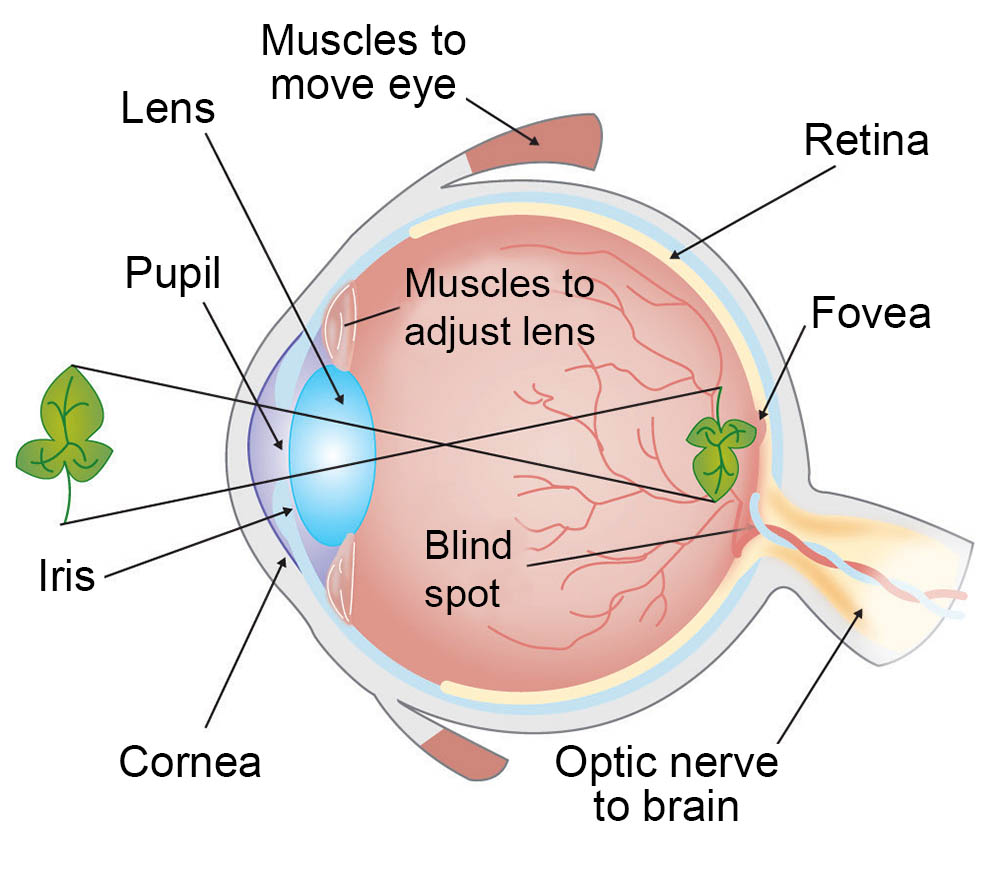
- Light enters the eye through cornea. The pupil appears black because no light is reflected from it. The eye lens is a convex lens made of a transparent jelly like material. The eye lens focuses the image of the object on the retina.
- There are two kinds of light sensitive cells on the retina:
- Cone shaped :- sensitive to colour.
- Rod-shaped :- sensitive to brightness or darkness or dim light
- If the image is formed in the blind spot part of the retina , the no signal is sent to the brain. As a result , the object is not seen.
- Even after the object is removed, the impression of an object seen by the eye remains on the retina for 1/16th of a second.This eye property is known as persistence of vision.
- There are three common eye defects, and they are(i) myopia or near-sightedness, (ii) Hypermetropia or far-sightedness, and (iii) Presbyopia. These defects are corrected by the use of suitable spherical lenses.
- Myopia can be corrected by using a spectacle of made from concave lenses.
- Hypermetropia can be corrected by using a spectacle of made from convex lenses.
- In old age, eye sight becomes foggy. This is called cataract. This can be corrected by a smile minor surgery.
- Deficiency of vitamin A leads to night blindness.

