Concepts
- Globalisation is the process of rapid integration and interconnection of countries.
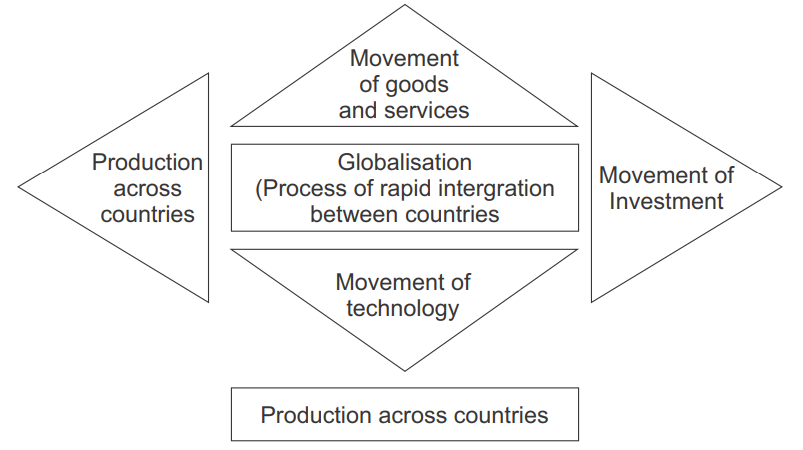
- Globalisation means integrating the economy of a country with the economies of other countries under conditions of free flow of trade and capital and movement of persons across borders.
- Integration of markets in different countries is known as foreign trade.
- Planning Commission in India has laid emphasis on the development of foreign trade in the five year plans due to the following reasons.
- A country can make efficient use of its natural resources :
- It can export its surplus production.
- Further, through effective regularisation of foreign trade, employment, output, prices and industrialisation, economic development of a country can properly accelerate.
- Investment made by Multinational Corporations (MNCs) is called foreign investment.
- MNCs are playing a major role in the process of rapid integration or interconnection between countries. Now more regions of the world are in closer contact with each other than a few decades back.
- MNCs play an important role in the Indian economy by setting up production jointly with some of the local companies. Example : MNCs can provide money for additional investments like buying new machines for faster production. Take another example - Cargil foods, a very large American MNC, has bought smaller Indian
companies such as Parakh Foods.
- How MNC’s interlink production across counties?
- MNC’s set up production unit where it is close to the market where skilled unskilled labour is available at low cost, where government policies are favourable.
- They invest money called foreign investment.
- At times set up production jointly with local companies.
- Benefits local companies by providing latest technology and additional investment.
They buy local companies and expand production. - Place orders to small producers for products like Garments, footwear sports items etc.
- How foreign trade leads to integration of markets?
- Foreign trade creates an opportunity for the producer to reach beyond the domestic market.
- Goods can be imported to expand the choice of goods for consumers.
- Producers in two countries now closely compete against each other, prices tend to become equal.
-
-
-
- Aim :- To liberalise international trade
- Started at the initiative of the developed countries
- Set up rules regarding international trade.
- Force developing countries to remove trade barriers
- Developed countries have unfairly retained trade barriers
- Aim :- To liberalise international trade
-
-
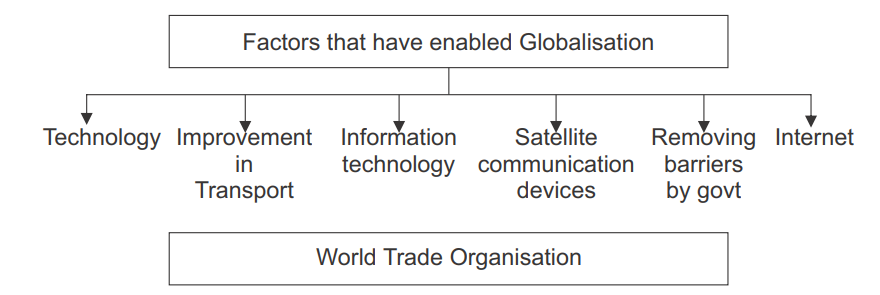
- Rapid improvement in information and communication technology has been one major factor that has stimulated the globalisation process. To access information instantly and to communicate from remote areas, devices such as telephones, mobiles and computers are very useful. Further, it has played a major role in spreading out production of services across countries.
- Impact of Globalisation
- For consumers:- Improved quality, lower prices, variety of choices, higher standard of living.
- Job have been created.
- Local companies supplying raw material to MNC’s have become prosperous.
- Top Indian companies have been benefitted from increased competition.
- Some Indian companies also emerged as MNC’s e.g. Tata Motor, Infosys, Ranbaxy, Asian Paints
- Impact of globalisation on the country is manifold. This can be understood by these examples.
- MNCs have increased their investment over the past 15 years, which is beneficial for them as well as for Indians also. This is because these MNCs provide employment opportunities to the masses and local companies supplying raw material to these industries have prospered. But globalisation has failed to solve the problem of poverty and it has widened the gap between the rich and the poor. Only skilled and educated class has benefited from
globalisation. - There is a greater choice for consumers, with a variety of goods and at cheap prices. Now they enjoy a much higher standard of living.
- MNCs have increased their investment over the past 15 years, which is beneficial for them as well as for Indians also. This is because these MNCs provide employment opportunities to the masses and local companies supplying raw material to these industries have prospered. But globalisation has failed to solve the problem of poverty and it has widened the gap between the rich and the poor. Only skilled and educated class has benefited from
- Struggle for a fair Globalisation
- Fair globalisation would create opportunities for all.
- The govt. must protect the interests of all the people in the country.
- Government can ensure that labour laws are properly implemented and workers get their rights.
- Government can negotiate at the WTO for farier rules.
- It can also align with other developing countries.
- Liberalisation of economy means to free it from direct or physical controls imposed by the government. In other words, it implies liberating the trade and industry from unwanted government control and restrictions.
- Liberalisation of foreign trade and foreign investment policy.
- Starting around 1991, barriers on foreign trade and foreign investments were removed to a large extent.
- It allowed foreign companies to set up factories and offices in India.
- Goods could be imported and exported easily.
- Let us see the effect of foreign trade through the example of Chinese toys in the Indian market. Chinese toys have become more popular in the Indian market because of their cheaper prices and new designs. Now Indian buyers have a greater choice of toys and at lower prices. Simultaneously, Chinese toy makers get the opportunity to expand business. On the other side, Indian toy makers face losses.
- World Trade Organisation (WTO) was started at the initiative of developed countries. The main objective of the World Trade Organisation is to liberalise international trade. At present 149 countries are members of the WTO.
- At present, central and state governments in India are taking special steps to attract foreign companies to invest in India. For this, Special Economic Zones (SEZs) are being set up. Special economic zones have world class facilities – electricity, telecommunication, broadband internet, roads, transport, storage and recreational facilities – to attract investment from MNCs and other companies.
- Globalisation and liberalisation have posed major challenges for small producers and workers. Small manufacturers have been hit hard due to competition. Several of the units have shut down rendering many workers jobless. Around 20 millions of workers are employed in small industries.
- Because of growing competition, most employers these days prefer to employ workers flexibly. This means that workers have no secure jobs. This can be explained with the help of an example : 35 year old Sushila got a job after searching for six months. She is a temporary worker. She did not get any benefit such as provident fund, medical allowance, bonus etc. A day off from work means no wage.
- Competition among the garment exporters has allowed the MNCs to make large profits, but workers are denied their fair share of benefits brought about by globalisation.
Key Points to Remember:
- Globalisation is a process of international integration arising from the interchange of world views, products, ideas and other aspects of a culture.
- Multinational Corporation (MNC) is an enterprise operating in several countries but Managed from one country or group that derives a quarter of its revenue from operations outside of its home country.
- Liberalization refers to the reduction or elimination of government regulation or restrictions on private business and trade.
- Investment is the purchase of goods (such as machine, house, and other parts etc.) that are not consumed today but are used in the future to create wealth.
- Foreign Trade is basically trade between two different countries of the world. It is also known as international trade.
- World Trade Organization is the only global international organization dealing with the rules of trade between nations. The main aim of this organization is to liberalize the law of trade between the nations.
- Privatization is the transfer of a business, industry, or service from public to private ownership and control.
- Foreign Investment is when a company or individual from one nation invests in assets or ownership stakes of a company based in another nation.
- SEZ is a special economic zone of a country that is subject to unique economic regulations that differs from other areas in the same country. These regulations tend to be conductive to foreign direct investment.

