Gender:-
- Sexual division of labour-all works inside the home done by women.
- Patriarchal society- all the power hold by men.
- Less representation in legislature (India)-approximately 11% in lok sabha in 2014.
- 1/3 reservation in local government
- Feminists and other people and many organisations are demanding for reservation of women in legislature.
Influence of Politics, Gender Caste and Religion on each other
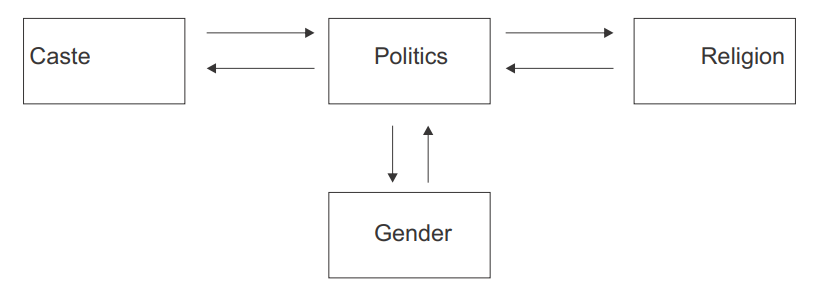
Memorable Facts :-
- Homogeneous Society –- A society that has similar kinds of people especially where there are no significant ethnic difference.
- African - American – The descendants of Africans who were brought into America as slaves between the 17th century and early 19th century.
- Apartheid – A policy or system of segregation or discrimination on grounds of race.
- Racism – Discrimination on the basis of colour of skin.
- Civil Rights Movement – It refers to a set of events and reforms movements aimed at abolishing legal racial discrimination against African - Americans
- Migrants – Anybody who shift from one region or country to another region within country or to another country for work or other economic opportunities.
- Scheduled Caste – Poor and landless and also socially and economically backward Indians.
- Sexual division of labour – A system in which all works are divided on the basis of sex. It means a particular work for a particular sex.
- Feminist – A woman or a man who believes in equal rights and opportunities for women and man.
- Patriarchy – A system of society in which men hold the power and women are largely excluded from it.
- Family laws – Those laws that deal with family related matters such as marriage, divorce, adoption etc.
- Secularism – The belief that religion should not be involved with the ordinary social and political activity of a country.
- Urbanisation – Shifting of population from rural areas to Urban areas.
- Occupational Mobility – Shift from one occupation to another.
- Caste hierarchy – A social structure in which classes are determined by heredity i.e. from the highest to the lowest castes.
- Universal adult franchise – After attaining a certain age, all the people are given right to vote without - discrimination of caste, class, colour, religion or gender.
- Communalism – A belief in which the followers of a particular religion believe that their religion is superior over other religion.
Public / Private Division
- In fact the majority of women do some sort of paid work in addition to domestic labour.But their work is not valued and does not get recognition.
- Although women constitute half of the humanity, their role in public life especially politics, is minimal in most societies.
- Women in different parts of the world organised and agitated for equal rights. There were agitation demanded enhancing the political and legal status of women and improving their educational and other opportunities. More radical women movements aimed at equality in personal and family life as well. These movements are called feminist
movements.
Patriarchal Society : Mostly societies are male dominating even day to day participation of women may increase than also our society is a patriarchal society on the basis of :- Literacy rate
- No wonder the proportion of women among the highly paid and valued jobs is still very small.
- Her work is not paid and therefore often not valued.
- Women are paid less than men.
- Girl child aborted before she is born.
- various kinds of harassment, exploitation and violence against women.
Religion, Communalism and Politics
- Unlike gender differences, the religious differences are often expressed in the field of politics.
- Communalism happens when beliefs of one religion are presented as superior to those of other religions, when the demands of one religious group are formed in opposition to another and when state power is used to establish domination of one religious group over the rest. This manner of using religious in politics is communal politics. Communalism can take various forms in politics :
- Stereo types of religious communities and belief in the superiority of one’s religion over other religions.
- A desire to form a separate political unit.
- Often involves special appeal to the interests in preference to others.
- Ugly form of communal violence, riots and massacre.
Secular State
- No official religion - constitution does not give a special status to any religion.
- freedom to profess, practice and propagate any religion.
- The constitution prohibits discrimination on ground of religion.
- allows the state to intervene is the matter of religion.
- ensure equality within religious communities.
Caste and Politics :
- They keep in mind the caste composition of the electorate and nominate candidates from different castes.
- Political parties and candidates in elections make appeals to caste sentiments to muster support.
- No parliamentary constituency in the country has a clear majority of one single caste.
- No party wins the votes of all the voters of a caste or community.
Questions:
1. How does communalism create problems in politics?
2. What are the effects of communalism on politics?
3. What is secularism? Mention any four provisions of the Indian Constitution which makes it a secular state.
4. Define a feminist movement. What is their objective?
5. How are religious differences expressed in politics?
6. How does the Constitution of India ensure secularism?
7. Explain the sexual division of labour.

