Concepts
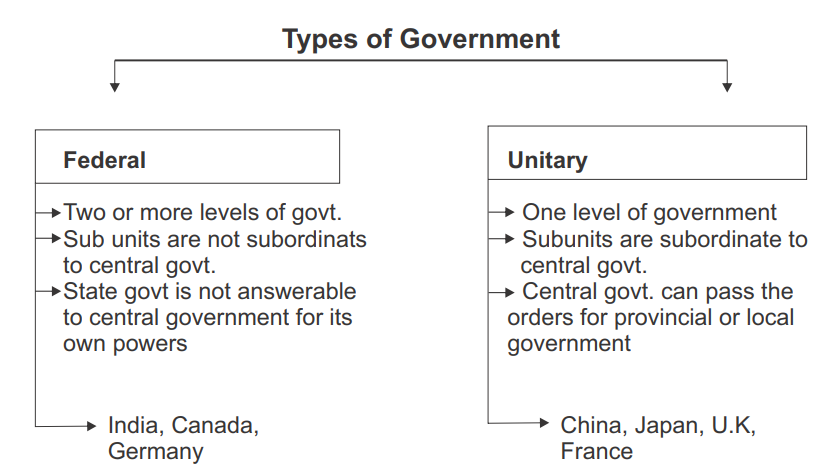
- In a federal system, power is divided at different levels. For example at the government level among the Executive, Legislature and Judiciary. At the government level among the central Government, state Government and Local Government. Each level of Government and its organs are free to work in their jurisdiction.
- On the other hand in the unitary form of Government, all the powers are rested in the hands of national government. In this system either there is one level of government or the sub-units are subordinate of central government. The central government can pass on orders to the provincial or local government. For example, Sri Lanka, China etc.
Features of Federalism
- There are two or more levels of Govt.
- Different tiers of Govt. govern the same citizens, but each tier has its own jurisdiction in pecific matters of legislation, taxation and administration.
- The jurisdictions of the respective levels or tiers of Govt are specified in the constitution.
- Require the consent of both the levels of Govt.
- Courts have the power to interpret the constitution and the powers of different levels of Govt.56
- An ideal federal system has both aspects : mutual trust and agreement to live together.
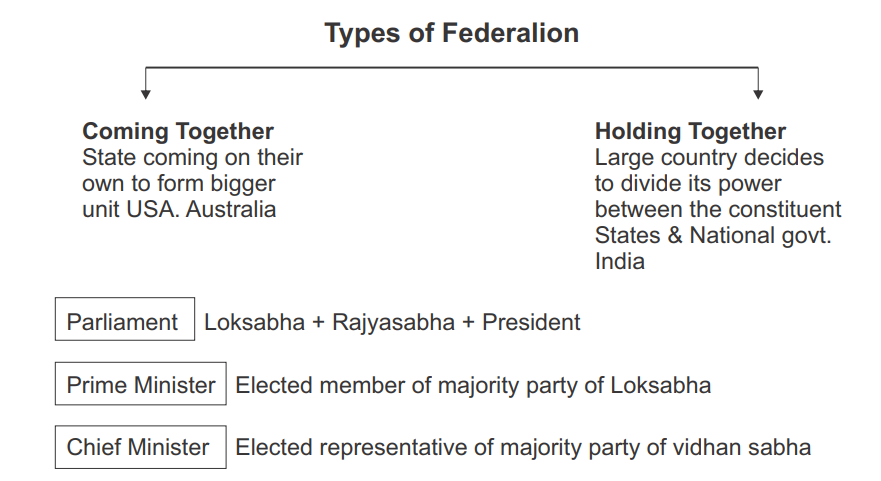
- The first route involves independent states coming together on their own to form a bigger unit.
- The second route is where a large country decides to divide its power between the constituent states and the national Govt.
Federalism in India
- The constitution originally provided for a two tier system of Govt the union Govt or what we call the Central Govt, representing the union of India and the state Govt. later, a third tier of federalism was added in the form of Panchayats and Municipalities.
- Constitution clearly provided a threefold distribution of legislative powers between the union Govt and the state Govt :
- Union list :- Defence of the country foreign affairs, banking.
- State List : Police, trade, commerce, agriculture.
- Concurrent List : Education, Forest, Trade Union, Marriage.
- Residuary Subject : Computer software - Only Jammu & Kashmir has their own constitution.
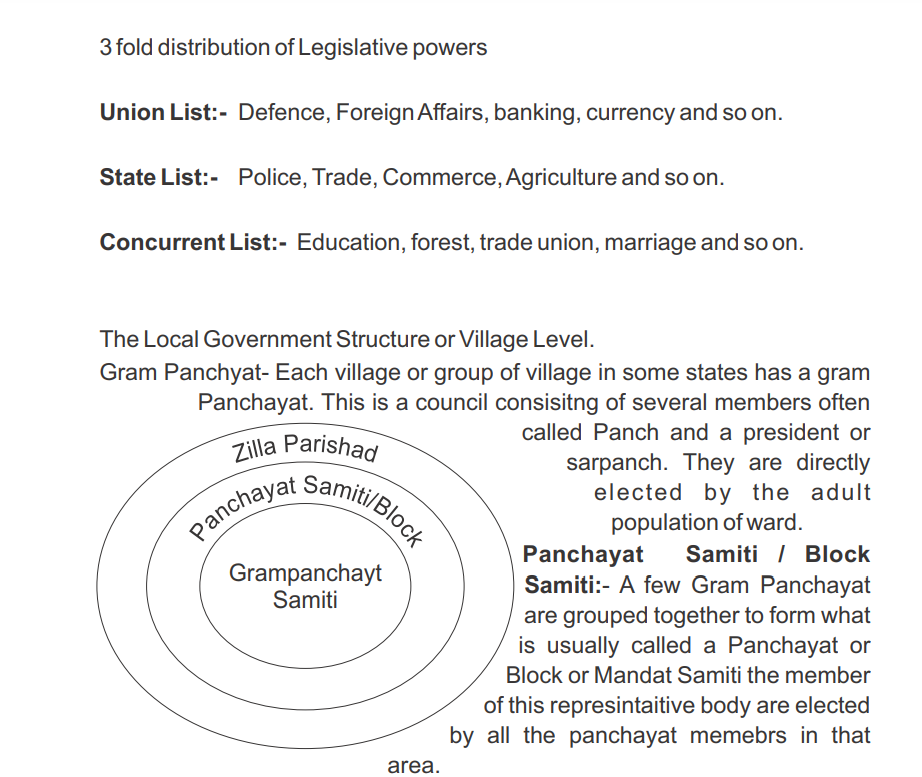
Zila Parishad:- All the Panchayat Samiti and Mandals in a district together constitute the Zila Parishad. Most of the mebers of Zila Parishad are elected.
Zila Parishad:- Members of loksabha + MLA's of that district & some other officials of other district level. Chairperson is the political head of Zila Parishad
Decentralization in India
- When power is taken away from central and State Govt. and given to local Govt. it is called decentralization.
- The basic idea behind decentralization is that there are a large number of problems and issues which are best settled at the local level.
- Local govt. gets constitutional importance in democracy.
- And representation of women may also increase with this role played by women in democracy became stronger.
Memorable Facts :-
- Horizontal distribution of power - Distribution of power among different organs of government such as the legislature, executive and judiciary.
- Vertical distribution of power – Distribution of power among government at different levels such as central government, Provincial Government, Local Government etc.
- System of check and balance – The system in which judges are appointed by the executive but they can check the functioning of executive or laws made by the legislators.
- Federalism: A system of government in which the power is divided between central authority and its various constituent units.
- In a federal system, the jurisdiction of the government of each level is clearly mentioned in the constitution.
- The fundamental provisions of the constitution cannot be unilaterally changed by one level of government in federalism.
- The objectives of federalism are not only to safeguard and promote unity of the country but also accommodate regional diversity.
- Coming together federations – When independent states come together on their own to form a bigger unit Ex- USA, Australia, Switzerland etc.
- Holding together federation – When a large country divides its power between the constituent states and the national government Ex- India, Spain, Belgium etc.
| Coming Together Federation | Holding Together Federation |
| 1. Under this, independent states come together on their own to form a bigger unit. | 1. Under this, a large country decides to divide its powers between the constituent units and the national government. |
| 2. All constituents states usually have equal powers and the states enjoy certain amount of autonomy | 2. Under this, central government tends to be more powerful. |
| 3. The main aim of the federation is to pool their sovereignty and maintain their separate identity to increase their security | 3. In this type of federation, there is an absence of pooling sovereignty and maintaining identity |
| Some examples are USA, Australia, and switzerland. | 4. Some examples are India,Belgium and Spain. |
- Jurisdiction – The area over which someone has legal authority.
- In India, the legislative powers have been divided into three lists.
- Union List – Subjects of national importance ex. foreign affairs banking, currency etc.
- State List – Subjects of state and local importance ex. - Police, trade, agriculture.
- Concurrent List – Subjects of common interests of both the union Govt as well as the state Govt.
- Residuary Subjects – The subjects which are not mentioned in Union, state or concurrent list come under the power of federal or union govt. and are called residuary subjects.
- Coalition Government – When two or more political parties com together to form a government.
- Hindi is the mother tongue of about 40% of Indians.
- Scheduled Languages : Such languages that come under eighth schedule of the Indian constitution.
- In 1992, a major step towards decentralisation was taken by making the third-tier of democracy powerful and effective.

