Concepts
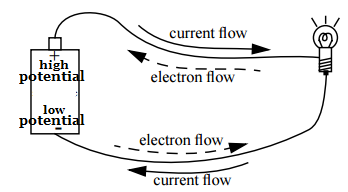
- Electric current is the flow of electricity through a conductor, such as a wire, and is measured in amperes (A).
- Electric current is the flow of electric charge (electrons) through a conductor.
-
Electric CircuitAn electric circuit is a closed conducting path that allows electric current to flow. It consists of a power source, conductors, and a load.
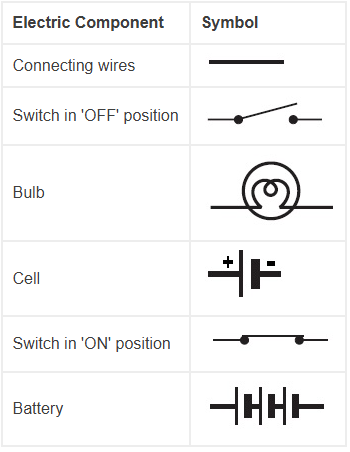
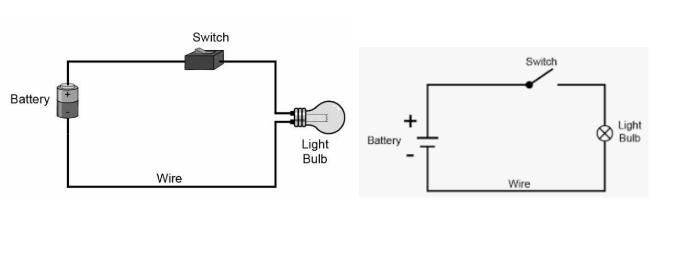 Electric Symbols
Electric Symbols
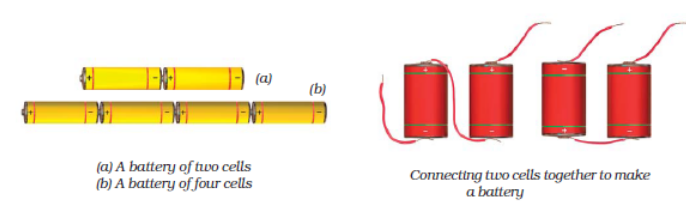
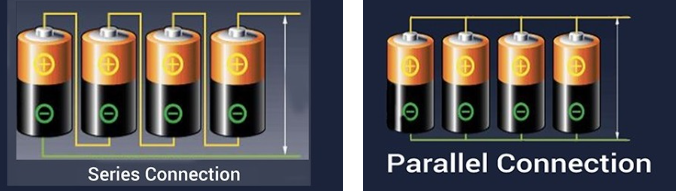
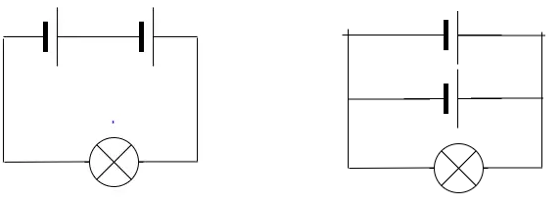
Combination of Electric Cells
Effects of Electric Current :
Electric current has several effects, including:
- Heating Effect of Electric Current: When electric current flows through a conductor, it generates heat. This effect is used in electric heaters, irons, and toasters.

-
- The generation of heat in a conductor when electricity passes through it is called heating effect of current.
- The heat produced in a conductor depends on the following factors:
- Current passed through the resister.
- Time for which the current is passes
- Nature of the material
- Applications:
- Electrical heating appliances
- Electric Filament Bulb
- Electric Fuse - is made from a low melting alloy , when large current passes through the circuit , this fuse wire gets heated up, and melt away . As a result , the circuit is broken and further damage to the electrical appliances is prevented.
- Light: Electric bulbs use the heating effect of current to produce light.
- Magnetic: Electric current can produce a magnetic field. This effect is used in electric bells, motors, and transformers.
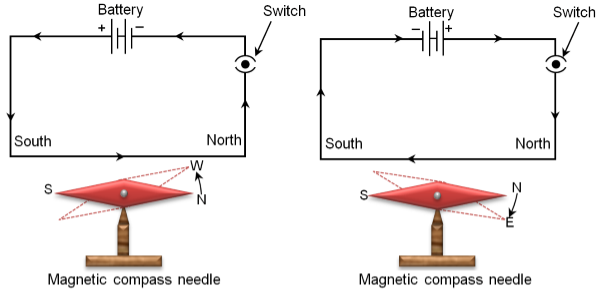
- When an electric current passes through a wire, it behaves like a magnet. This is the magnetic effect of the electric current. If the electric current does not passes through, it loses its magnetic effect. These coils of wire are called electromagnets.
-
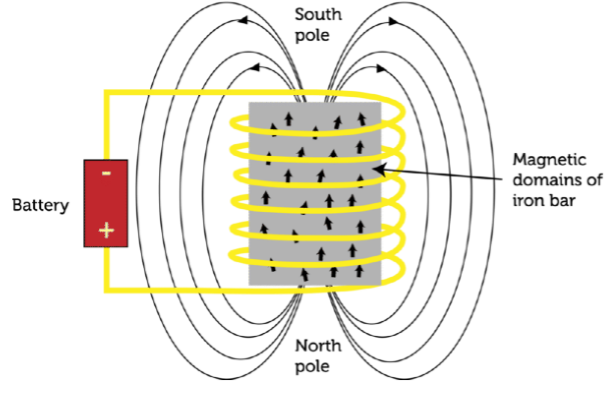
- An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. Electromagnets usually consist of wire wound into a coil. A current through the wire creates a magnetic field which is concentrated in the hole in the center of the coil.
-
- Applications:
- For lifting heavy loads
- In hospital for removing iron splinters from the eyes.
- For separating magnetic substances from nonmagnetic substances
- In instruments i.e. electric bells , telegraphic and telephonic systems , speakers etc.
- Applications:
- What is an Electric Bell?
-
- An electromechanical device that works with the help of an electromagnet is called an electric bell. In a classic bell, on applying an electric current, the to and fro movement of a small hammer on a gong would produce the sound of a bell. Thus, an electric bell is an electric device generally used for signalling the presence of a guest or visitor.
- These days the electric bells even play songs or tunes when rung. Since the 19th century, these mechanical-electric bells have been widely used in schools, burglar alarms, railway crossings, telephones and industries. An invention of its kind, the electric bell, is widely used as electronic sounder worldwide. An electric bell consists of an electromagnet attached to a strip of iron that makes the hammer hit the gong, thereby producing the ringing sound.
-
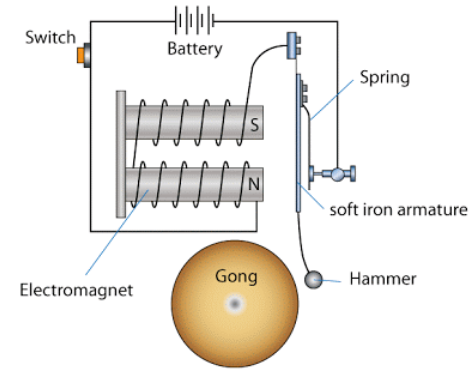
- Principle of Working of an Electric Bell
- The working of an electric bell is based on the principle of electromagnetism or the magnetic effect of the current. According to the phenomena of electromagnetism, magnetic fields are associated with moving electric charges. Whenever an electric current flows through a conductor, the magnetic field is generated. The direction of this magnetic field can be determined using the right-hand-thumb rule. Electromagnets are constructed using this principle. Electromagnets are widely used in electrical devices like televisions, radios, speakers and even an electric bell.
- Construction of an Electric Bell
- An electric bell consists of a gong, an electromagnet, a soft iron rod and a contact screw. Electromagnet plays a very crucial role in the construction of an electric bell. Let us learn a little detail about electromagnets.
Electromagnet: An electromagnet is an artificial magnet in which the flow of current produces an electric field. An electromagnet consists of a wire wound in a coil. When an electric current passes through the wire, it generates a magnetic field around it, and the wire behaves like an electromagnet. The magnetic field around an electromagnet lasts as long as there is current flowing through the wire. The strength of the magnetic field of an electromagnet can be increased by increasing the number of turns in the coil, increasing current through the coil and wounding this coil around a magnetic material like soft iron. An electromagnet behaves essentially like a normal magnet as long as there is electric power across its ends. When the electric power is switched off, the magnetic field around the electromagnet disappears.
- An electric bell consists of a gong, an electromagnet, a soft iron rod and a contact screw. Electromagnet plays a very crucial role in the construction of an electric bell. Let us learn a little detail about electromagnets.

