Networking Concepts
- Computer Network: A group of computers & other peripheral devices that are all linked togethers for the purpose of sharing data and hardware resources.
- Node: Each computer in a network is called a Node.
Computer Network as a Data Communication System
Components of Data Communication
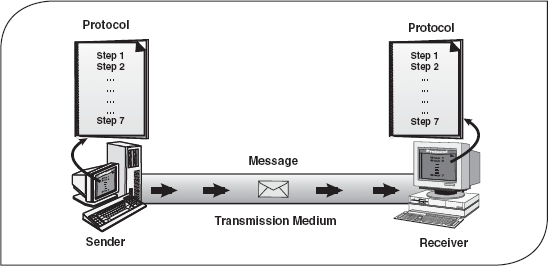
- Message : Message is the information to be communicated by the sender to the receiver.
- Sender : The sender is any device that is capable of sending the data (message).
- Receiver : The receiver is a device that the sender wants to communicate the data (message).
- Transmission Medium : It is the path by which the message travels from sender to receiver. It can be wired or wireless and many subtypes in both.
- Protocol : A Protocol is defined as a set of rules that governs data communications. A protocol defines what is to be communicated, how it is to be communicated and when it is to be communicated.
Networking Media
- Wired : Ethernet Cable , Coaxial Cable , Optical Fiber Cable
- Wireless: Bluetooth , Infrared , Wi-Fi
Types of Networks
- PAN ( 10 m ) , 1 Computer
- LAN ( 100 m ) , 2 or more Computer
- CAN ( Campus Area Network )
- WAN ( two or more computers at distant places.)
Networking Devices
- Modem: to connect computer to the internet over existing telephone line.
- Hub: to connect multiple computers & devices by using cables.
- Switch: Similar to hub, but offer greater performance
- Repeater : used to regenerate a signal.
- Router: used to connect two different networks.
- Gateway: acts as an entrance to another network using different protocols.
- Bridge : Similar to repeater with add-on functionality of filtering content.
Networking Terminology
- Internet : A global wide area network that connects computers across the world.
- Intranet: A computer network with in an organization.
- Bandwidth: The amount of data that can be transmitted in a fixed amount of time.
- ISP : Service provider that provides internet connection.
- Website: A collection of webpages containing images , videos and texts.
- Web Portal: A gateway or entrance to the access of information.
- Web Page: A digital page which contains text , hyperlink, videos , audios, images, tables etc..
- Home Page: First page of website.
- Link: a line or channel to connect two devices.
- Hyperlink: A link that connects one webpage to another webpage.
- URL: Unique Address of a webpage or a website.
- IP Address: A unique (32 bit) set of numbers, which is provided to each computer by IETF.
- Domain Name: A unique name given to each website.
- TCP/IP: A suite of communication protocols used to connect various computers on the internet.
- TCP: used for a reliable data transmission over the network.
- IP: Provides a sequence numbers to each data packets so that they can reach their destination.
- HTTP: A protocol that defines what actions web servers and browsers should take in response to various commands.
- FTP: A protocol to exchange files between two or more computers on the internet.
Review Python
Python : Python is a programming language which takes input, process and provide output.
- Features of Python:
- Simple & Interactive
- Platform Independent
- Case Sensitive
- Object Oriented
- Interpreted Language
- Uses variables without declaration
Working Mode of Python
- Interactive mode ( the interpreter executes the statements one by one )
- Script Mode ( Displays the results of expressions )
Types of Commands in Interactive Mode:
- print ( ) function : to print output.
- " , " ( comma ) : to print the next value after a space.
- "\t" (tab ) : to print the new value in the next line.
- type ( ) function: to return the data type of a value.
- Input ( ) function: to store a value in a variable.
Variables: a , b , c etc. are variables used to store the values.
Data Types in Python:
- int : used when you have to work with whole numbers ( +ve or -ve ) , Example: 1500 , -1986
- float : represents floating point values. Example : 709 , 789 , 17.234
- string : Represents a collection of characters enclosed within single or double quotes. Example: Python_Language
- bool: 124<987
Arithmetic Operators in Python:
- Unary Operators : They work on a single operand. Ex. ( a=10 , a=-10 )
- Binary Operators: They work on two operands. Ex. ( a=30 , b =20 )
- Addition (+) : to add data values . (Ex. , 30+20=50)
- Subtraction (-) : to find difference of the data value ( Ex. 100-30=70 )
- Multiply (*) : to find product of the data value ( Ex. 10*2= 20 )
- Division ( /) : to divide the numbers and give results in decimal form. ( Ex. 10/4=2.5)
- Integer Division (//): to divide the numbers and give results in integer form.( Ex. 10//4=2)
- Modulus ( % ): to divide the numbers and give the remainder. ( Ex. 10%3=1 )
- Exponential ( **): to find the powers of the numbers. ( 3**4=81 )
Precedence of operators:
- ( ) : Parenthesis
- ** : Exponentiation
- +X ,-X : +Unary , -Unary
- * , / , // , % : Multiplication, Division, Floor Division, Modulus
- + ,- : Binary Addition , Subtraction
- < , > , <= , = , = = , != : Rational Operators
- not and or : Boolean /Logical operators
Conditional Statements:
if statement
if << condition>:
statements set
Example of Program:
a=int ( input ( input ("Enter a number :")
b=int ( input ( input ("Enter another number :"))
if a==b:
print ( " The numbers are equal ")
Output
Enter a number :34
Enter another number :34
The numbers are equal
if...else statement
if << condition>:
statements set 1
else
statements set 2
Example of Program:
a=int ( input ( input ("Enter the first number :")
b=int ( input ( input ("Enter the second number :"))
if a>b:
print ( a, "is greater than" , b )
else:
print ( b, " is greater than " a )
Output
Enter the first number :456
Enter the second number :234
456 is greater than 234
Iterative Statements : The statements that keep repeating themselves as long as a given condition. These are slso called Repetitive statements or looping statements.
In Python , there are two types of Iterative statements:
for : used when we are sure about how many times a loop body will be executed. Also known as definite loop.
The syntax for using the for loop is:
for < variable > in <
- while :

