Key Concept
Understand basic fundamentals
- Chemistry: a branch of science which deals with composition , structure and properties of matter.
- Matter: Anything which occupies space and has mass.The quantity of matter is its mass.
- Chemical Substance: Any material with a known chemical composition.
- Classification of Matter:
- Physical Classification
- Chemical Classification
- Physical Classification:
- Solids : They have a Volume & shape. Ex.: wood , sugar , gold etc.
- Liquids: They have a Volume but no shape. Ex.: water , oil , milk etc.
- Gases : They have no fixed Volume or shape. Ex.: O2, N2, H2 etc..
- Chemical Classification:
- Mixtures: contain more than 1 substance in any proportion.
- Homogeneous Mixtures : which have uniform composition throughout. It can not be seen even with a microscope. Ex. sugar , glucose , salt , urea etc.
- Heterogeneous Mixtures :which do not have uniform composition throughout. It can be seen with a microscope. Ex.: oil, water , cement, sand , iron , sulphur , rice , wheat , mud etc..
- Pure substance: Have definite composition.
- Elements: which contains only one kind of atoms. Ex. Copper, Silver, Gold, oxygen , nitrogen etc...
- Compounds: which contains two or more atoms of different elements. Ex. CO2 , H2O , NH3 , SO2,
- Mixtures: contain more than 1 substance in any proportion.

Elements:
- It is the simplest form of the matter.
- Smallest unit of an element is known as atom.
- Total number of the known elements is 118 out of which 98 elements occur naturally and 20 are formed by artificial transmutation.
- Examples: Na, K, Mg. Al, Si, P, C, F, Br etc.
Compound:
- It is a non-elemental pure compound.
- Formed by chemical combination of two or more atoms of different elements in a fixed ratio.
- Examples: H2O, CO2, C6H12O6 etc.
Mixture:
- Formed by physical combination of two or more pure substances in any ratio.
- Chemical identity of the pure components remains maintained in mixtures.
- Homogeneous mixtures are those whose composition for each part remains constant.
- Example, Aqueous and gaseous solution.
- Heterogeneous mixtures are those whose composition may vary for each and every part.
- Example, Soil and concrete mixtures.
Structure of Atoms
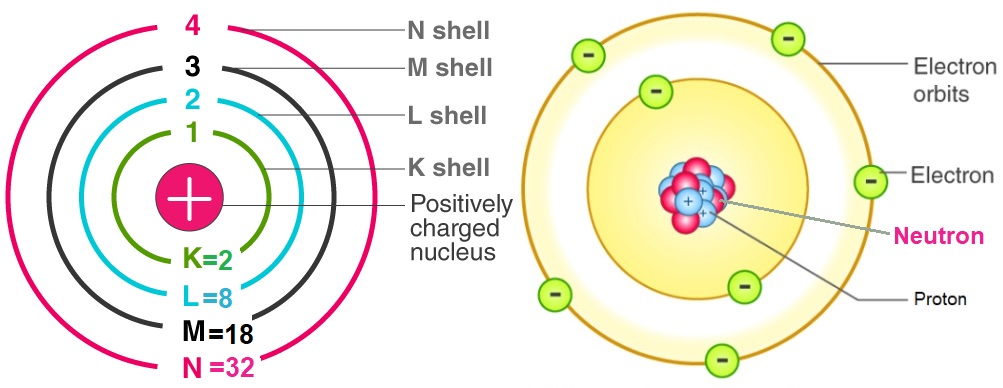
Calculation of number of proton:
- The protons are positively charged particles present in the nucleus of an atom.
- The number of proton in an atom is equal to the atomic number of that element.
- Thus, Number of protons=Atomic number (Z)
Calculation of number of electron:
- The electrons are negatively charged particles that revolve in the shells around the nucleus.
- The number of electron in a neutral atom is equal to the atomic number of that element.
- Thus, Number of electrons in a neutral atom=Atomic number (Z)
Calculation of number of neutron:
- The neutrons are electrically neutral particles present in the nucleus of an atom.
- The mass number is the sum of the number of protons and number of neutrons of the element.
- Thus, the number of neutrons can be calculated from the mass number of the element.
- Thus, Number of neutrons=Mass number (A) - Atomic number (Z)
Example: Carbon (C) atom:
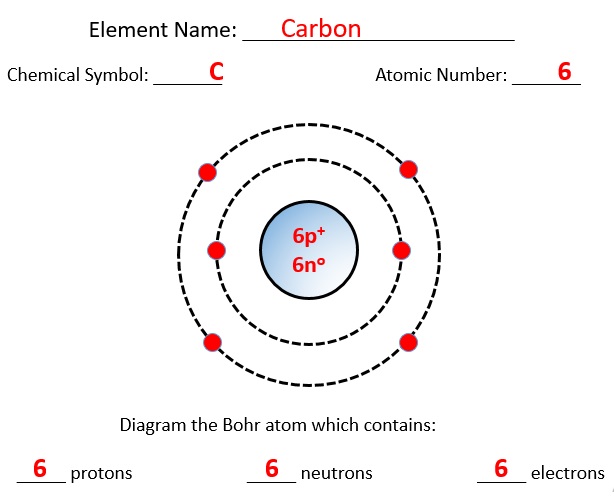
Atomic number of an element = No of electrons in one neutral atom = 6
The atomic number of Carbon is 6. Thus, Number of protons=Number of electrons=6
∴ The mass number of Carbon = No. of proton + No of neutron = 6 + 6 = 12
Thus, Number of neutrons= Mass No. - Atomic Number = 12-6=6
Thus, the number of protons, electrons and neutrons in a Carbon atom are 6, 6 and 6 respectively.

