Key Concept
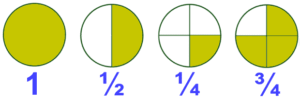
- A Fraction is a part of whole. The ‘whole’ here could be an object or the group of objects. But all the parts of the whole must be equal.
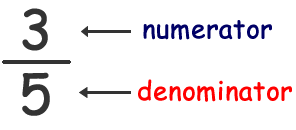
- Numerator and Denominator
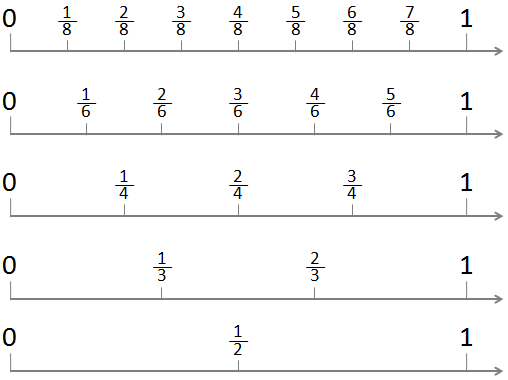
- Proper Fractions :If the numerator is less than the denominator then it is called proper fraction. If we represent a proper fraction on the number line than it will always lie between 0 and 1. Examples

- Improper fraction : When the numerator is greater than the denominator then it is called Improper fraction. Ex.: 5/4
- Mixed fraction:The fraction made by the combination of whole and a part is called Mixed fraction. Ex. : 2(1/2)
- Convert Mixed fraction into Improper fraction
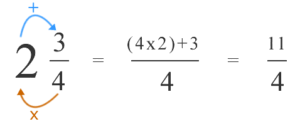
- Equivalent Fractions: Equivalent fractions are those fractions which represent the same part of a whole.
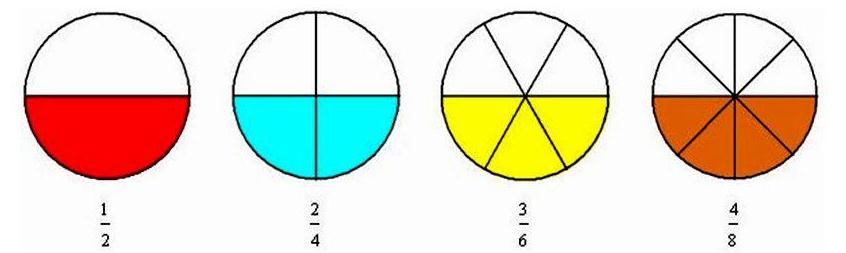
- Finding equivalent fractions
- By Multiplying the same number in Numerator and Denominator
- By Dividing the same number in Numerator and Denominator
- Like Fractions:Fractions which have same denominators are known as Like fractions.
Example : 
- Unlike fractions: Fractions which have different denominators are known as unlike fractions.
Example :
- Comparing like fractions :Fraction with the small denominator is greater than the other.
![]()
![]()
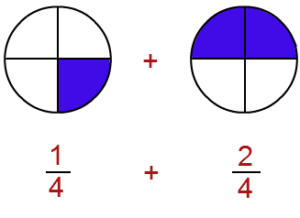
- Addition and Subtraction of Fractions