concept
WATER
- It is one of the most important resources for us. The three-fourth part of the earth is composed of water near about 71%.
- Almost 97% of water is salty found in the oceans. However, we need freshwater to survive which is only 3 %, and in that 3%, 2% freshwater is found in glaciers and ice caps completely frozen.
- About 0.6% of freshwater is present deep under the ground from the total water present on earth.
- About 0.009% of freshwater is found in rivers, lakes and springs from the total percentage of the water.
Where does water come from?
- People living in different regions have different sources of the water that they use. While some draw it from wells, ponds and lakes directly, others like many of us receive water through taps via a network of pipes connected to these lakes, ponds and rivers.
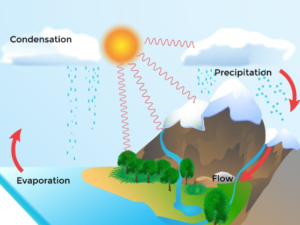
Water Cycle:-
1) Evaporation
Evaporation is the process of converting liquid or water into a gaseous form or vapour state.
2) Condensation
The process of converting vapour or gaseous form into its liquid form is called condensation.

3) Precipitation
When more water gets condensed in clouds, or condensation of water vapour in the atmosphere results in precipitation. The precipitation can be in the form of rain, snow, or hail.

Drought
- Rainfall is the main source of getting water. During the summer season, the weather conditions start becoming hot. As a result, the process of evaporation and transpiration frequently increased which causes the loss of water.
- Due to some reason, rain does not occur for a long time causes a shortage of water. Moreover, the water of lakes, ponds and rivers start drying. This leads to a condition or disaster called drought.

Flood
-
- Rainfall brings about life, but excess rainfall leads to an increase in water levels in water bodies like rivers and ponds.
- Adverse effects of floods:
- Flood causes damage to human life, crops, domestic animals and animals living in the water.
- This excess water may spread over large areas causing floods.
What if it Rains Heavily?
-
The excess rainfall increases the water level in water bodies which leads to floods.
-
Flood is the overflow of water which submerges land causing destruction.
-
Floods cause loss of livelihoods by washing away people and animals.
-
It also provides damage to infrastructures and disrupts the supplies of clean water causing a situation of water scarcity.
What Happens if it Does Not Rain for A Long Period?
-
No rainfall can decrease the water level in water bodies and ground water level also decreases due to excess transpiration which leads to drought.
-
Drought is the situation when there is no water available for even drinking, the complete dryness is drought.
-
Drought leads to the shortage of water supplies eventually leads to loss of livelihoods.
How Can We Conserve Water?
-
Out of surplus water present we have access to only a small fraction of water.
-
With an increasing population, the demand for water consumption is also increasing.
-
The increased demand for water consumption and careless use of this natural resource leads to shortage of water.
-
We must adopt some measures to conserve water.
-
Sustainable use of water can help us to save water for the future also.
Ground Water
The water present underground or beneath the earth’s surface in spaces of soil and rocks is called groundwater.
Water level
Level of water or is the height reached by the water in lakes, ponds, storage tanks, and dams.
Infiltration
The process of water seeping into the soil after falling onto the surface of the ground is called infiltration.
Aquifers
An aquifer is the underground layer of permeable rock which contains water that has seeped in from the surface.
-
-