Concepts
- Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter.
- Different kinds of matter exist because there are different kinds of atoms present in them.
- Charged Particles in Matter
Whenever we rub two objects together, they become electrically charged. This is because atoms contain charged particles in them. Therefore, atoms can be divided further into particles i.e proton, electron and neutron. - Protons were discovered by Ernest Rutherford, in his famous gold foil experiment.
- Electrons were discovered by J.J. Thomson, in his cathode ray tube experiment.
- Neutrons were discovered by James Chadwick.
- Atoms consist of protons and electrons in a balanced proportion.
- Protons exist in the interiors of the atom and electrons exist in the exteriors of the atom. Therefore, electrons can be removed from an atom.
Failure of Dalton’s Atomic Theory
- The postulates of the atomic theory by John Dalton
- The matter is made up of tiny particles called Atoms that cannot be divided.
- Atoms are never formed or destroyed during a chemical reaction.
- Atoms of an element exhibit same nature. They have the same size, mass, and character.
- Atoms of different elements exhibit variant nature. They do not have same characteristics.
- Atoms form compounds by combining in a ratio of whole numbers.
- A compound contains a constant number and kinds of atoms
- Dalton suggested that atoms can neither be created nor destroyed and are indivisible. But the discovery of electrons and protons in atoms lead to failure of this aspect of Dalton’s theory.
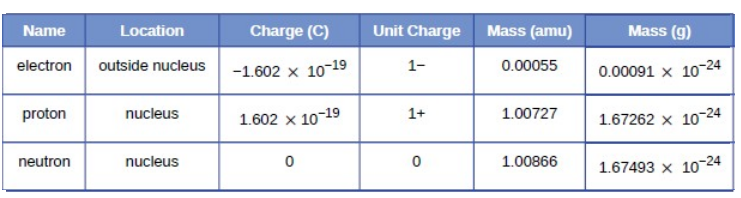
Thomson’s Model of an Atom
According to J.J. Thomson, the structure of an atom can be compared to Christmas pudding where electrons are present inside a positive sphere. According to Thomson's Mode:
- An atom is composed of a positively charged sphere in which electrons are embedded.
- Atom is neutral as the positive and negative charged are equal in proportion.
Rutherford’s Model of an Atom
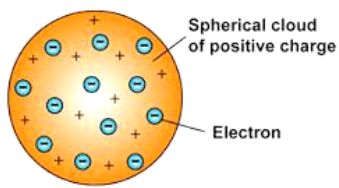
Rutherford’s Experiment
- He experimented with thin gold foil by passing alpha rays through it.
- He expected that the gold atoms will deflect the Alpha particles.
| Observations | Inferences |
| Alpha particles which had high speed moved straight through the gold foil | Atom contains a lot of empty space |
| Some particles got diverted a by slide angles | Positive charges in the atom are not occupying much of its space |
| Only one out of 12000 particles bounced back | The positive charges are concentrated over a particular area of the atom. |
Thus, Rutherford gave the nuclear model of an atom based on his experiment which suggests that -
- Atoms contain a lot of unoccupied space
- There is a heavily positively charged substance present in the center of the atom which is called the nucleus
- The nucleus contains an equal amount of positive and negative charge.
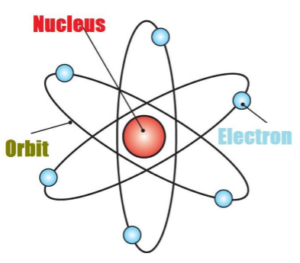
The Nucleus of an Atom
- The nucleus is located at the center of the atom.
- All the mass of the atom is because of the nucleus.
- The electrons revolve around the nucleus in circular parts which are called Orbits
- If we compare the size of the atom and nucleus, the nucleus is much smaller than the atom.
Drawbacks of the Nuclear Model of an Atom
The Nuclear Model of the Atom failed to explain how an atom remains stable despite having positive and negative charges present in it. Maxwell has suggested a theory according to which if any charged particle moves in a circular motion it radiates energy. So, if electrons start moving in a circular motion around the nucleus they would also radiate some energy which would decrease at the speed of the electrons. As a result, they would fall into the nucleus because of its high positive charge.
What are nucleons? – Protons and Neutrons are collectively called as Nucleons.
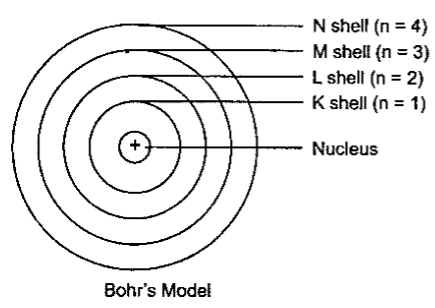
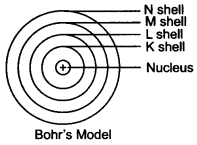
Bohr's Model of an Atom
Bohr suggested that –
- Electrons spin around the nucleus in an individualized separate path or unattached orbit.
- The electrons do not emit any energy while moving Indies special orbits.
- These orbits are also called as Energy Levels.
- They are represented using letters or numbers as shown in the figure below –
The Neutrons
J. Chadwick discovered that there is another sub-atomic particle present in the atom. This particle carries no charge and is known as a Neutron. Therefore, we can conclude that atom consists of three types of particles -
| Electrons | which carry a negative charge |
| Protons | which carry a positive charge |
| Neutrons | they are neutral |
The distribution of electrons in different shells or orbits
- If Orbit number = n
- Then number of electrons present in an Orbit = 2n2
- So, for n =1
- Maximum electrons present in shell – K = 2 * (1)2 = 2
- The outermost shell can contain at most 8 electrons.
- The shells in an atom are filled in sequence.
- Thus, until the inner shells of an atom are filled completely the outer shells cannot contain any electrons.
Valency
- Valence Electrons – Electrons existing in the outermost orbit of an atom are called Valence Electrons.
- The atoms which have completely filled the outermost shell are not very active chemically.
- The valency of an atom or the combining capacity of an atom is given by the number of elements present in the outermost shell.
- For Example, Helium contains two electrons in its outermost shell which means its valency is two. In other words, it can share two electrons to form a chemical bond with another element.
- What happens when the outermost shell contains a number of electrons that are close to its maximum capacity?
Valency in such cases is generated by subtracting the number of electrons present in the outermost orbit from octet (8). For example, oxygen contains 6 electrons in its outermost shell. Its valency is calculated as: 8 – 6 = 2. This means oxygen needs two electrons to form a bond with another element.
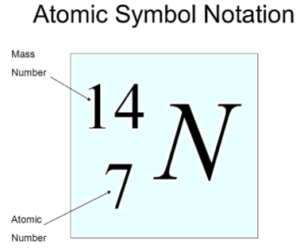
Atomic Number of an Element
Atomic Number (Z) = Number of protons in an atom
Mass Number of an Element
Mass Number = Number of protons + Number of neutrons
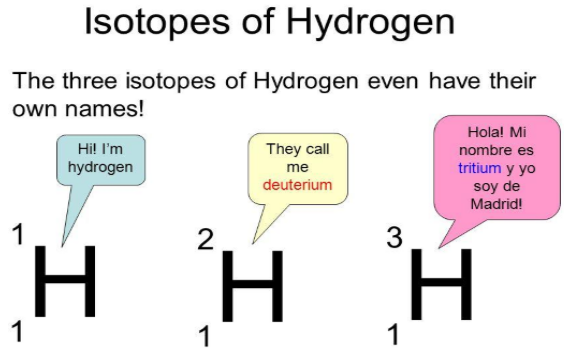
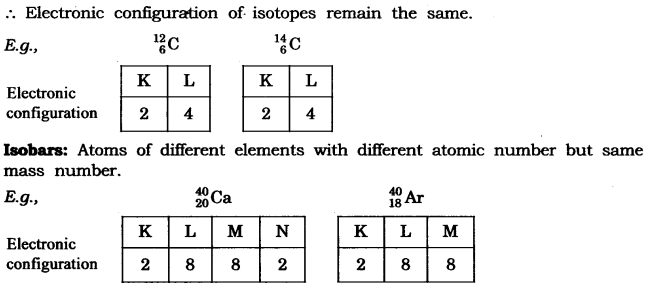
Isotopes
- The atoms of an element can exist in several forms having similar atomic numbers but varying mass numbers.
- Isotopes are pure substances.
- Isotopes have a similar chemical nature.
- Isotopes have distinct physical characteristics.
Where can we use Isotopes?
1. The fuel of Nuclear Reactor – Isotope of Uranium
2. Treatment of Cancer – Isotope of Cobalt
3. Treatment of Goiter – Isotope of Iodine
Example: Consider two atomic species namely U and V. Are they isotopes?
| U | V | |
| Protons | 5 | 5 |
| Neutrons | 5 | 6 |
| Mass Number | 5 + 5 = 10 | 5 + 6 = 11 |
| Atomic Number | 5 | 5 |
From the above example, we can infer that U and V are isotopes because their atomic number is the same.
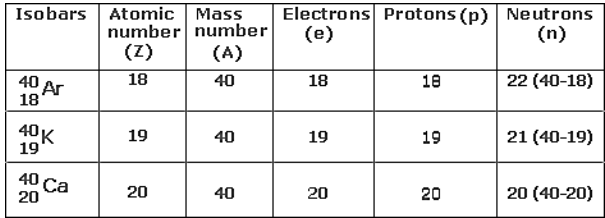
Isobars
The atoms of several elements can have a similar mass number but distinct atomic masses. Such elements are called Isobars.
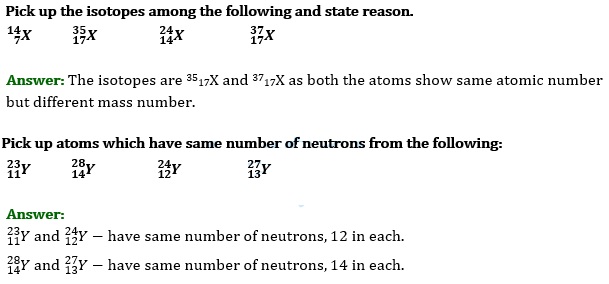
Number of neutrons in 2311X.
Answer: Mass number = 23
∴ p + n = 23 , p = 11 , (Atomic No. = Number of protons)
∴ 11 + n = 23
∴ n = 12
∴ Neutron =12
Number of neutrons in 2713X.
Answer: Mass number = 27
∴ p + n = 27 , p = 13 , (Atomic No. = Number of protons)
∴ 13 + n = 27
∴ n = 13
∴ Neutron =14
Questions & Answers
Draw the atomic structure of hydrogen atom.
Answer:
Why is atom electrically neutral?
Answer: It has same number of protons and electrons, (positive charge = negative charge).
What is the charge and mass of a-particles?
Answer: Charge is + 2
Mass is 4 a.m.u.
What are valence electrons?
Answer: Electrons present in the outermost shell of an atom are called valence electrons.
An atom has atomic number 12, what is its valency and name the element?
Answer: Atomic number = 12
∴ Protons = Electrons = 12 Electrons Configuration = K L M -2 8 2
∴ Valency = 2
Element is magnesium.
Find the number of neutrons in 2713X.
Answer: Mass number = 27
∴ p + n = 27 p = 13, (Atomic No. = Number of protons)
∴ 13 + n = 27
∴ n = 14
∴ Neutron =14
Where is the mass of atom is concentrated?
Answer: Mass of an atom is concentrated in nucleus.
Name two elements with same number of protons and neutrons?
Answer: Carbon (Protons = Neutrons = 6)
Oxygen (Protons = Neutrons = 8)
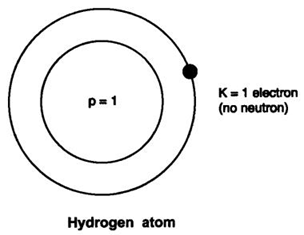
Draw the atomic structure of sodium atom.
Name the isotope used for treatment of cancer.
Answer: Isotope of cobalt.12: AZX What does this symbol represent?
Answer: X → Symbol of element
A → Mass number
Z → Atomic number
Can the value of ‘Z’ be same for two different atoms?
Answer: No, (Z = atomic number), two different atoms cannot have same atomic number.
Can the value of A’ be same for two different atom?
Answer: Yes, it can be e.g. Ca and Ar has A-40 (i.e., mass number).
Name the scientist who discovered protons and neutrons in an atoms.
Answer: Protons were discovered by E. Goldstein in 1866 and neutrons were discovered by J, Chadwick in 1932.
What is the contribution of Bohr and Bury together in the structure of atom’s explanation?
Answer: Both Bohr and Bury gave the distribution of electrons into different atoms by giving the formula 2n2, where n = shell number.
Draw the atomic structure of (i) an atom with same number of sub-atomic particles, (ii) an atom with same number of electrons in L and M shell.
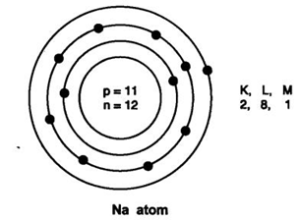
Answer: (i) An atom with same number of sub-atomic particles is He
No. of protons = 2
No. of electrons = 2
No. of neutrons = 2
(ii) An atom with L and M shell filled → K ,L ,M= 2, 8 ,8
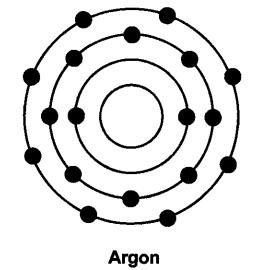
What is an octate? Why would atoms want to complete their octate?
Answer: When the outermost shell of an atom i.e., L, M or N are completely filled with 8 electrons in the shell, it is said an octate. Atoms would want to complete their octate because they want to become stable.
Find the valency of 147N and 3517Cl.
Answer: The atomic number of nitrogen = 7, No. of protons = 7, No. of electrons = 7
Electronic configuration = K L M = 2 5 –
Valency = 3
Because either it will gain three electrons or share 3 electrons to complete its octate.
The atomic number of chlorine = 17, p = 17, e=17
Electronic configuration = K L M= 2 8 7
Valency = 1
Because it will gain 1 electron to complete its octate.
What are nucleons? What is the name given to those atoms which have same number of nucleons in it?
Answer: Protons and neutrons present in the nucleus are called nucleons Isobaric elements have same number of nucleons in it.
| Element | Protons | Neutrons | (Protons + Neutrons) |
| Argon | 18 | 22 | 40 |
| Calcium | 20 | 20 | 40 |
| Potassium | 19 | 21 | 40 |
Give the difference between three sub-atomic particles.
Answer: Three sub-atomic particles are electron, proton and neutron

Give the names of three atomic species of hydrogen.
Answer: Three atomic species of hydrogen are:
| Name | Protium | Deuterium | Tritium |
| Symbol | 11H | 21H | 31H |
| Protons | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Atomic no. | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Neutrons | 0 | 1 | 2 |
Atomic Mass exists as whole number, why do we write the atomic mass of chlorine as 35.5 u.
Answer: Chlorine has two isotopes and the mass of an atom is taken as the average mass of all the naturally occurring atoms of that element.
This is obtained by knowing the percentage of each isotopic from and then the average mass is calculated Cl = 35 – 75% and Cl = 37 – 25% = 35.5 u
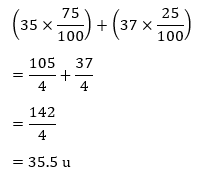
Give difference between isotopes, and isobars.
Answer:
| Isotopes | Isobars |
| Are atoms of same element. | Are atoms of different element |
| Have same atomic number | Have different atomic number |
| Have different mass number | Have same mass number |
| Number of protons and electrons are same in these atoms. | Number of protons and electrons are not same in these atoms. |
Number of protons and electrons are same in an atom. Then why is it wrong to say that atomic number of an atom is equal to its number of electrons.
Answer: Atomic number ≠ Number of electrons, although number of protons = number of electrons because the electron’s number can change in an atom by loss, or gain of it. But the proton’s number remain constant (as it does not take part in loss or gain).
An atom is electrically neutral, on loss or gain of electrons why does it become charged?
Number of protons ≠ Number of electrons
If it loses electrons p > e; hence +ve charge is obtained.
If it gains electrons e > p; hence -ve charge is obtained.
What is valency? Explain different types of valencies.
Answer: The combining capacity of an atom is called its valency. There are 2 types of valencies.
| Covalency | Electrovalency |
| When an atom share electrons have combining capacity. | When an atom loses or gains electrons |
Some atoms also show zero valency when there outermost shell is completely filled.
NCERT Questions
Question: On the basis of Thomson’s model of an atom, explain how the atom is neutral as a whole.
Answer: According to Thomson’s model of an atom
(i) An atom consists of a positively charged sphere and the electrons are embedded in it,
(ii) The negative and positive charges are equal in magnitude. So the atom is electrically neutral.
Question:On the basis of Rutherford’s model of an atom, which sub-atomic particle is present in the nucleus of an atom?
Answer: As per Rutherford’s model of an atom, the protons which are positively charged are present in the nucleus of an atom.
Question ; Draw a sketch of Bohr’s model of an atom with three shells.
Answer:
Question:. What do you think would be the observation if the a-particle scattering experiment is carried out using a foil of a metal other than gold?
Answer: On using any metal foil, the observations of the a-particle scattering experiment would remain the same as all atoms would have same structure.
Question : Name the three sub-atomic particles of an atom.
Answer: The sub-atomic particles of an atom are
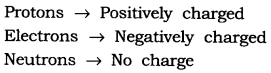
Question: Helium atom has an atomic mass of 4 u and two protons in its nucleus. How many neutrons does it have?
Answer:
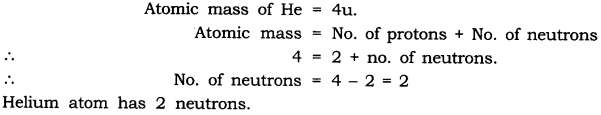
Question :. Write the distribution of electrons in carbon and sodium atoms.
Answer:

Question :. If K and L shells of an atom are full, then what would be the total number of electrons in the atom?
Answer: K shell can hold 2 electrons and L shell can hold 8 electrons. When both the shells are full, there will be (8 + 2) 10 electrons in the atom.
Question:. How will you find the valency of chlorine, sulphur and magnesium?
Answer:


Question . If number of electrons in an atom is 8 and number of protons is also 8, then
(i) What is the atomic number of the atom? and
(ii) What is the charge on the atom?

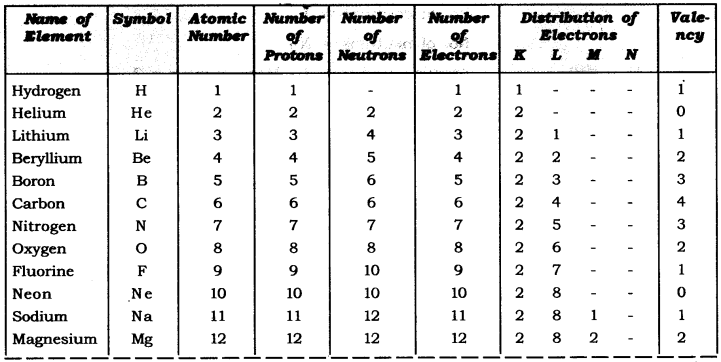
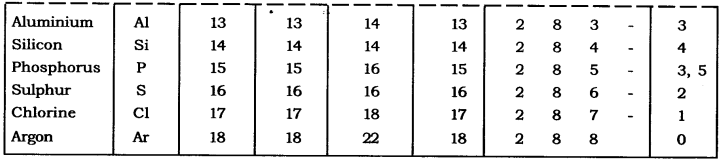
Question :. With the help of given Table 4.1, find out the mass number of oxygen and sulphur atom.
Table: Composition of Atoms of the First Eighteen Elements with Electron Distribution in Various Shells
Question . Write the electronic configuration of any one pair of isotopes and isobar.
Answer. Isotopes: Atoms of same element having same atomic number but different mass number.
Question:. If bromine atom is available in the form of say, two isotopes 7935Br (49.7%) and 8135Br (50.3%), calculate the average atomic mass of bromine atom.
Answer:

Question:. The average atomic mass of a sample of an element X is 16.2 u. What are the percentages of isotopes 168X and 188X in the sample?
Answer: Let the percentage of 168X be x and the percentage of 168X be 100 – x.

Question: A sample of an element A contains two isotopes 168A and 188A. If the average atomic mass of the element is 16.2 amu, calculate the percentage of the two isotopes in this sample.
Answer:
Let, the percentage of 168A be X and
percentage of 188A be 100-X
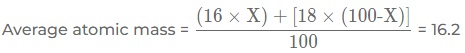
⇒ 16X + 1800 - 18X = 1620
⇒ -2X + 1800 = 1620
⇒ -2X = 1620 - 1800
⇒ 2X = 180
⇒ X = 18022180 = 90
∴ 100 - X = 100 - 90 = 10
Hence, percentage of the two isotopes in this sample are 90% of 168A and 10% of 188A

