Concepts
Heron’s formula, formula credited to Heron of Alexandria (c. 62 CE) for finding the area of a triangle in terms of the lengths of its sides. In symbols, if a, b, and c are the lengths of the sides: Area = Square root of√s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)where s is half the perimeter, or (a + b + c)/2.
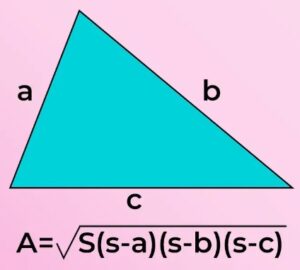
A = √{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}
Where,
- A is area of Triangle ABC,
- a, b, c are lengths of the sides of the triangle, and
- s is semi-perimeter = (a + b + c)/2.
Area of a Triangle = (1/2) × b × h
Where,
- b is the base, and
- h is the height.
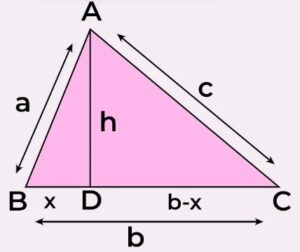
Draw a perpendicular AD on BC
From the ∆ ABD,
a2 = x2 + h2
⇒ x2 = (a2−h2)….(i)
⇒ x = √(a2−h2)….(ii)
Consider the ∆ACD,
(b−x)2 + h2 = c2
⇒ (b−x)2 = c2 − h2
⇒ b2 − 2bx + x2 = c2–h2
Putting the value of x and x2 from equations (i) and (ii) in the above equation, we get
b2 – 2b√(a2−h2)+ a2−h2 = c2 − h2
⇒ b2 + a2 − c2 = 2b√(a2 − h2)
Squaring on both sides, we get;
(b2 + a2 – c2)2 = 4b2(a2−h2)
⇒ {(b2 + a2 – c2)2) / 4b2 = (a2−h2)
⇒ a2 + {(b2 + a2 – c2)2) / 4b2 = h2
simplifying, we get
h2 = (a+b+c)(b+c-a)(a+c-b)(a+b-c) / 4b2
Now, 2s = a+b+c, where s is the semi-perimeter of the triangle.
h2 = 2s(2s-2a)(2s-2b)(2s-2c) / 4b2
⇒ h = √[2s(2s-2a)(2s-2b)(2s-2c)] / 2b
⇒ h = 2×√[s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)] / b…(iii)
From, area of triangle = 1/2 × b × h
Now, area of triangle = 1/2 × {b × 2×√[s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)]} / b
Area of Triangle (A) = √[s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)]
Heron’s Formula for Equilateral Triangle
For an equilateral triangle, all sides are equal. Now, the semi-perimeter of the equilateral triangle is
s = (a+a+a) / 2
⇒ s = 3a / 2
where a is the length of the side.
Now, using Heron’s Formula,
Area of Equilateral Triangle = √(s(s – a)(s – a)(s – a)
Area of Equilateral Triangle = √3 / 4 × a2
Heron’s Formula for Scalene Triangle
Area of scalene triangle ABC(A) = √s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)
Where s is the semi-perimeter i.e., s = (a + b + c)/2.
Heron’s Formula for Isosceles Triangle
rea of iscosceles triangle ABC(A) = √s(s-a)(s-a)(s-b)
Where s is the semi-perimeter i.e., s = (a + b + c)/2.
Simplifying, A = √s(s-a)(s-a)(s-b)
⇒ s = a + b/2
⇒ A = √s(s-a)(s-a)(s-b)
⇒ A = √(a + b/2)(b/2)(b/2)(a – b/2)
⇒ A = √(a + b/2)(a – b/2)(b/2)(b/2)
A = √[(a2 – b2/4)(b2/4)]
Solved Examples on Heron’s Formula
Example 1: Calculate the area of a triangle whose lengths of sides a, b, and c are 14cm,13cm, and 15 cm respectively.
Solution:
Given:
a = 14cm
b = 13cm
c = 15cmFirstly, we will determine semi-perimeter(s)
s = (a + b + c)/2
⇒ s = (14 + 13 + 15)/2
⇒ s = 21 cmThus, A = √(s(s – a)(s – a)(s – a)
⇒ A = √(21(21 – 14)(21 – 13)(21 – 15)
⇒ A = 84 cm2
Example 2: Find the area of the triangle if the length of two sides is 11cm and 13cm and the perimeter is 32cm.
Solution:
Let a, b and c be the three sides of the triangle.
a = 11cm
b= 13 cmc = ?
Perimeter = 32cm
As we know, Perimeter equals to the sum of the length of three sides of a triangle.
Perimeter = (a + b + c)
⇒ 32 = 11 + 13 + c
⇒ c = 32 – 24
⇒ c= 8 cm
Now as we already know the value of perimeter,
s = perimeter / 2
⇒ s = 32 / 2
⇒ s =16 cm
As, a = 11cm, b = 13 cm, c = 8 cm, s = 16 cm
Thus, A = √(s(s – a)(s – a)(s – a)
⇒ A = √(16(16 – 11)(16 – 13)(16 – 8)
⇒ A = 43.8 cm2
Example 3: Find the area of an equilateral triangle with a side of 8 cm.
Solution:
Given,
Side = 8 cm
Area of Equilateral Triangle = √3 / 4 × a2
⇒ Area of Equilateral Triangle = √3 / 4 × (8)2
⇒ Area of Equilateral Triangle = 16 √3 cm2
Important Example: The perimeter of a triangular field is 540 m and its sides are in the ratio 25 : 17 : 12. Find the area of the triangle.
Perimeter of a triangle = 540 m
Ratio in sides = 25:17:12
Sum of ratios = 25+17+12=54
∴ First side = (540×25)÷ 54=250m
Second side = (540×17)÷54=170m
Third side = (540×12)÷ 54=120m
or 25x+17x+12x=540
54x=540
∴ x=540÷54=10
∴ First side = 25*10=250m
Second side = 17*10=170m
Third side = 12*10=120m
∴ s=Perimeter÷2=540÷2=270
∴Area=√s(s−a)(s−b)(s−c)
=√270(270−250)(270−170)(270−120) m2=√270×20×100×150
=√3×3×3×2×5×5×2×2×10×10×2×3×5×5 m2
=3×3×2×5×2×10×5=9000 m2

