Concepts
- Agriculture is a primary activity, which produces most of the food raw material for various industries.
- Two-thirds of India’s population is engaged in agricultural activities because of following reasons:
- Agriculture is a primary activity and produces most of the food and food grains.
- It produces raw materials for our various industries, e.g., cotton textile, sugar industry.
- Agricultural products, like tea, coffee, spices are exported and earn foreign exchange.
- Agriculture: The science and art of cultivation on the soil , raising crops and rearing livestock. It is also called farming.
- Sericulture : Commercial rearing of silk worms. It may supplement the income of the farmer.
- Pisciculture: Breeding of fish in specially constructed tanks and ponds.
- Viticulture : Cultivation of grapes.
- Horticulture: Growing vegetables , flowers and fruits for commercial use.
- Farm System:
- Inputs: Machinery , Seeds , Chemicals
- Processes: Plouging , Sowing , Spraying , watering , weeding , harvesting , threshing
- Outputs: Crops
- Types of Farming :
- Subsistence Farming : Practised to meet the needs of the farmer's family.
- Intensive Subsistence Farming: farmer cultivates a small plot of land using simple tools. ex. Rice, wheat , maize, pulses and oilseeds. in the thickly populated areas of the monsoon regions.
- Primitive Subsistence Farming: practiced in few pockets of India and depends upon monsoon and soil.
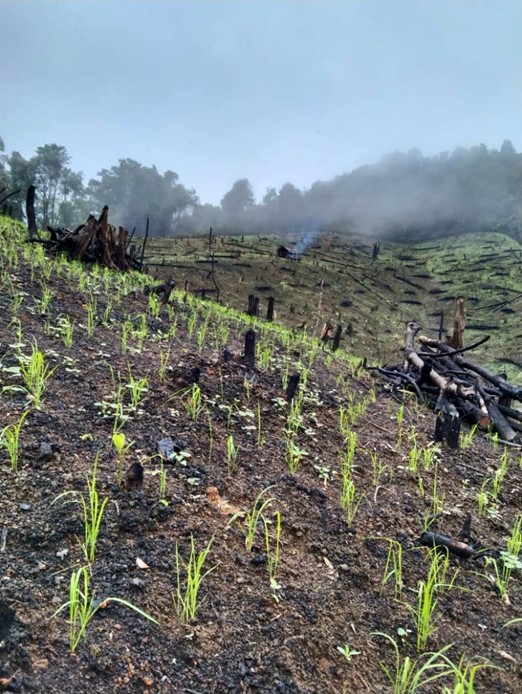
- Shifting Cultivation: practiced in the thickly forested areas of Amazon basis, tropical Africa and parts of south east Asia and northeast Asia. Also known as " slash and burn " agriculture.
- Subsistence Farming : Practised to meet the needs of the farmer's family.

-
-
-
- Nomadic Herding : practised in the semi-arid and arid regions of Sahara, Central Asia and some parts of India like Rajasthan , J&K. In this type of farming herdsmen move from place to place with their animals for fodder and water.
-
-

-
- Commercial Farming : Crops are grown and animals are reared for sale in market. Most of the work is done by machines. Wheat and maize are common commercially grown grains.
- Plantations are a type of commercial farming where single crop of tea , coffee, sugarcane, cashew, rubber , banana and cotton are grown mainly in the tropical regions. Rubber in Malaysia , coffee in Brazil , Tea in India & Srilanka.
- Mixed farming : and is used for growing food and fodder crops and rearing livestock.
- Organic farming : organic manure and natural pesticides are used instead of chemicals.
- Commercial Farming : Crops are grown and animals are reared for sale in market. Most of the work is done by machines. Wheat and maize are common commercially grown grains.
- Cropping Pattern
- Rabi crops : sown in winter from October to December and harvested in summer from April to June.
- Kharif crops : sown in the beginning of the rainy season between April and May and harvested in September-October.
- Zaid season is the short period during the summer months in between the rabi and the kharif seasons.
- Major Crops:
- Rice : a kharif crop, It requires high temperature, (above 25°C) and high humidity with annual rainfall above 100 cm. China leads in the production of rice followed by India. Favaourable climatic conditions in West Bengal and Bangladesh where two to three crops are grown in a year.
- Wheat : a rabi crop and is the second most important cereal crop. It requires moderate temperature and rainfall. Grown extensively in USA , Canada , Argentina , Russia , Ukraine , Australia and India.
- Millets : coarse grains and can be grown on less fertile and sandy soils. it requires low rainfall and high to moderate temperature. Jowar , bajra and ragi are grown in India. Other countries are Nigeria, China , Niger.
- Maize: It requires well drained fertile soils. moderate temp , rainfall and lots of sunshine. Grown in North America , Brazil, China , Russia , Canada, India and Mexico.
- Cotton: It requires high temperature , light rainfall , two hundred and ten frost free days and bright sunshine. It grows best on black and alluvial soils. China , USA , India , Pakistan , Brazil and Egypt are leading producer.
- Jute : Known as " Golden Fibre ". It grows in alluvial soils. requires high temperature , heavy rainfall and humid climate. India and Bangladesh are leading producers of jute.
- Coffee: Coffee requires warm and wet climate and well drained loamy soil. Hill slopes are more suitable for growth of this crop. Brazil is the leading producer followed by Columbia and India.
- Tea: a beverage crop grown on plantations. require cool climate and well disturbed high rainfall throughout the year for the growth of its tender leaves. It needs well-drained loamy soils and gentle slopes. Labour in large number is required to pick the leaves. Kenya , India , China , Srilanka produce the best quality tea in the world.
- Food Security
- The primary objective of the India’s food security policy is to ensure availability of food grains to the common people at an affordable price.
- It has enabled the poor to have access to food and focuses on growth in agriculture production and on fixing the support price for procurement of wheat and rice, to maintain their stocks.
- It consists of two components:
- Buffer stock
- Public distribution system (PDS)
- Food Corporation of India (FCI) is responsible for procuring and stocking foodgrains, whereas distribution is ensured by public distribution system (PDS).
- Consumers are divided into two categories – below poverty line (BPL) and above poverty line (APL).
Q: What is agriculture?
Ans: Agriculture is the primary activity that involves the cultivation of crops, fruits, vegetables, flowers and rearing of livestock.
Q: Name the factors influencing agriculture.
Ans: Factors influencing agriculture include the topography of soil and climate.
Q: What is shifting cultivation? What are its disadvantages?
Ans: Shifting cultivation is the type of farming in which agricultural activities are shifted from one field to another when the fertility of the soil of the former is diminished.
Disadvantages:
- Deforestation
- Soil erosion
- Small patches for cultivation
- Not sufficient for feeding a large population.
Q: What is plantation agriculture?
Ans: Plantation agriculture is a type of commercial farming where only a single crop (like tea, coffee, sugarcane, cashew, rubber, banana or cotton) is grown. A large amount of labour and capital are required. The product is processed on the farm itself or nearby factories.
Q: Name the fibre crops and name the climatic conditions required for their growth.
Ans:Two major fiber crops are jute and cotton. Jute grows well on alluvial soil and requires high temperature, heavy rainfall, and a humid climate for its growth. Cotton needs high temperatures, light rainfall, and bright sunshine for its proper growth.
Q: In India agriculture is a primary activity. Why?
Ans: Agriculture is an activity of growing crops, fruits, vegetables, flowers, and rearing of livestock. It is a primary activity since it directly involves natural resources. In India, a huge number of people derive the activity from their ancestors. Due to lack of literacy in general, farmers prefer agriculture since they acquire the required skills from their ancestors, and so feel comfortable with it.
Q: Different crops are grown in different regions. Why?
Due to :
Different topography
Different soils
Different climates
Different lifestyles of the people in different regions.
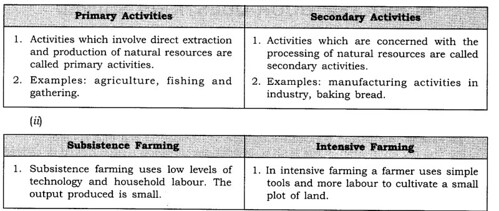
Q: Distinguish between the following.
(i) Primary activities and secondary activities.
(ii) Subsistence farming and intensive farming.