Concepts
Understand fundamentals
- Matter: that occupies space and has a mass. It can be anything.
- Element: All matter is made up of the substances called element, which has specific chemical and physical properties. Element is the basic unit which can't be decomposed further by any kind of reaction.
- Compound: When elements are combined chemically in a fixed ratio, it is called as compound. For example H2S is a compound where H and S are elements.
- Atom: Atom is a tiny particle of any matter made up of sub atomic particles known as protons, neutrons, and electrons. An atom is made up of a nucleus surrounded by one or more electrons.
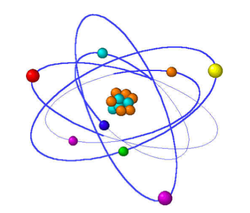
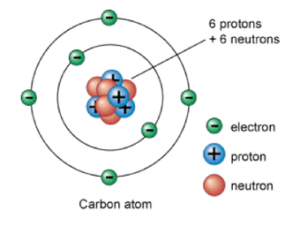
- Proton: It is a sub atomic particle which is positively charges and it is present inside of nucleus.
- Neutron: It is a sub-atomic particle which does not carry any charge.
- Electron: It is a sub atomic particle which is negatively charges and it is present outside of nucleus. Electrons revolve rapidly around nucleus in fixed circular paths called energy levels or shells. These energy levels of elements are also called orbits. The representation of the orbits is done by letters and numbers such as K, L, M, N, O…. and 1,2,3,4…. respectively.
- Rule 1: The maximum number of electrons present in a particular shell is calculated by the formula 2n2, where “n” represents the shell number. For instance, the K shell is the first shell and it can hold up to 2(1)2 = 2 electrons. Similarly, the L shell is the second shell and it can hold up to 2(2)2 = 8 electrons. This formula helps to calculate the maximum number of electrons that an orbit can accommodate.
- Rule 2: The maximum capacity to hold electrons in the outermost shell is 8.
- Rule 3: The electrons will fill the inner shells before the outer shells. First electrons will fill the K-shell and then L shell and so on. Thus, the electronic configuration of elements follows an ascending order.
- The electronic configuration of an atom is the number of electrons it has arranged by energy level.
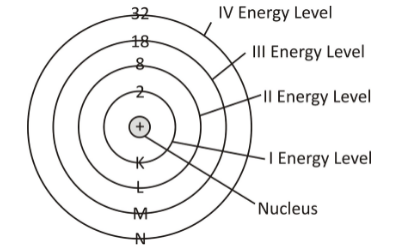
| Shell and ‘n’ value | Max. Electrons in the Electron Configuration |
| K shell, n=1 | 2*12 = 2 |
| L shell, n=2 | 2*22 = 8 |
| M shell, n=3 | 2*32 = 18 |
| N shell, n=4 | 2*42 = 32 |
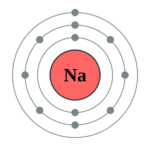
For Example: Electronic configuration of Sodium : 2, 8 , 1
- How to find element valency?
- The electron present in the outer most cell are called valency electron. If valency electron are greater than "4 " , then the valency of an element is determined by substracting total number of electrons present in the outer most cell from "8".
- For example: Electronic configuration of Chlorine ( Cl) is : 17 = 2 , 8 , 7 . Since it has 7 ( more than 4 ) electrons in its outer most cell, therefore valency of Cl = 8 - ( no. of electrons in the outermost cell ) = 8-7 = 1
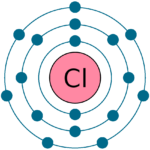
-
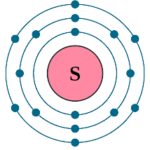
- Electronic configuration of Sulphur ( S) is : 16 = 2 , 8 , 6 . Since it has 6 ( more than 4 ) electrons in its outer most cell, therefore valency of Cl = 8 - ( no. of electrons in the outermost cell ) = 8-6 = 2
- Making formula by valency transfer:
- Step 1 : H S
- Step 2: 1 2
- Step 3: Cross-over the valences
- Formula: H2S ( Hydrogen Sulphide )
- Ions: Ions are charged particles. When an atom or a group of atoms lose or gain electrons, they are converted into ions or radicals. The two types of ions are cations (+) and anions (-).
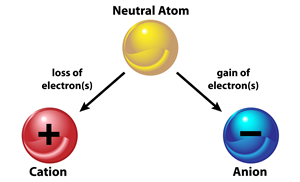
- Cations: Positively charged ions , Anions: Negatively charged ions.
- Formation of ions: Except the noble gases, the valence shells or the outermost orbits in atoms of most elements have one to seven electrons. So, these atoms either donate or accept electrons in their outer shells to attain the stable electronic configuration of nearest noble gas. Due to the transfer of negatively charged electrons, the atom that donates electrons becomes positively charged, while the atom that gains electrons becomes negatively charged. These charged particles are called ions. When an atom has one to three electrons in its valence shell, it loses one or more electrons to attain the stable electronic configuration of nearest noble gas. Since it loses negatively charged electrons, it becomes positively charged ion. Such positively charged ions are called cations.
- Formation of Sodium ion
Atomic number of sodium is 11, it has following electronic configuration: 2(K), 8(L), 1(M).
Sodium atom donates one electron in its valence shell ‘M’, which results in disappearance of ‘M’ shell and its ‘L’ shell with eight electrons becomes new valence shell. Thus, it attains the stable electronic configuration of nearest noble gas – neon.
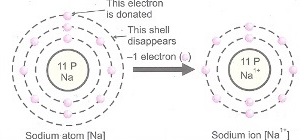
Na → Na+ + e–
Mock Test
Test your knowledge

